

iConsole Search Definition Reference Guide › Search Architecture
Search Architecture
iConsole searches and reports comprise a number of components:
- Database Stored Procedures (SPs)
-
Define the query logic that is executed and the results that are returned.
- Search Definitions
-
XML documents that define the properties of the search that form the inputs that the SP requires and the layout of the results from the SP. The Search Definition can also include scripting to define behavior for the properties or results displays.
- Script Files
-
In addition to inline script in the XML, you can load script from separate script files. This can be useful when the script is used by several searches or reports, reducing duplication.
- Help Files
-
You can provide help files for both the properties and results pages to guide the user on how to provide the required inputs, and how to interpret the results.
- Report Format Files
-
You can produce custom reports by specifying an XSL file to transform the raw results into the required report format. This can be further processed into a document format (such as PDF) if required.
This section contains the following topics:
Architecture
Search Execution
Architecture
The iConsole is a Web Application that you access using a web browser (such as Internet Explorer). The program logic is distributed across four logical systems:
- The Browser provides the presentation layer of the application. The iConsole display is primarily generated using javascript on the user’s workstation. Requests are made to the Web Server using AJAX.
- The Web Server manages the user’s session, delivering resources such as web pages, script files and images, and manages requests for CA DataMinder information through a SOAP interface.
- The Application Server provides Web Services that encapsulate the business logic of the iConsole. The Web Services are called upon by the Web Server to deliver information from the CA DataMinder database via the CA DataMinder Infrastructure.
- The CMS manages the CA DataMinder database and responds to the requests from the Application Server.
Each of these systems can be hosted on separate computers, all installed on the same computer or any other configuration to meet the performance needs of the business.
As far as iConsole search components are concerned:
- The Database Stored Procedures and Search Definitions are installed on the CMS.
- Script Files and Help Files are installed on the Web Server
- Report Format Files are installed on the Application Server.
Search Execution
The following diagram illustrates the typical search execution:
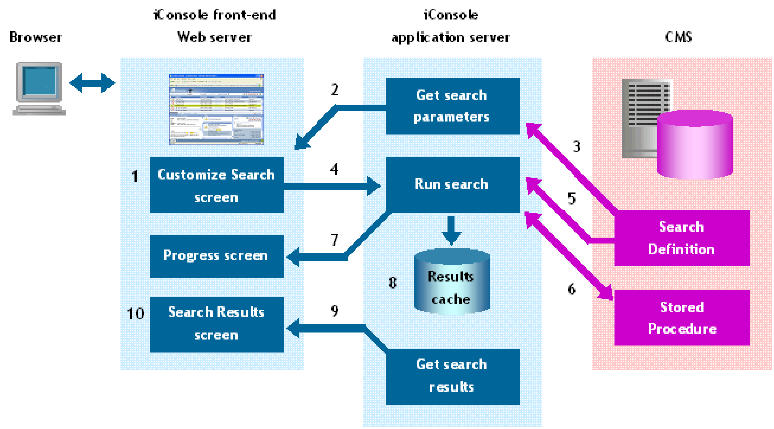
- The user selects the search to be run. An AJAX request is made to the Web Server for the search details. The Web Server sends a SOAP request to the Application Server for the Search Definition. The Search Definition is retrieved from the CMS and delivered to the Web Browser. The Browser renders the parameters defined in the Search Definition for the user to edit.
- The user enters values for the parameters and clicks Run. The browser sends the parameters to the Web Server which makes a request to run the search to the Application Server. The Application Server starts a thread to run the search and returns immediately. The browser displays a progress dialog, periodically polling to see if the search is complete and updating the progress.
- The Application Server thread merges the supplied parameter values with the Search Definition and runs its stored procedure by making a request to the CMS. When the search is complete, the results are retrieved and packaged for return to the browser, along with results display details from the Search Definition. The results are temporarily stored in the Application Server cache.
- When the progress indicates that the results are ready, the Web Browser requests the results from the Web Server and it makes a request to get the results from the Application Server cache. The results are returned to the Browser which renders them, using the display details, for the user to review. Paging, filtering and sorting of results is all performed in the browser (with the exception of unlimited searches).
More information:
Supporting Searches of Unlimited Size
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


