

CA DataMinder can integrate with EMC Corporation's Centera content addressed storage (CAS) solution to ensure long-term content integrity and online access for large volumes of fixed data. Integration between these two systems provides your enterprise with an end-to-end solution to your email and Web risk management and storage needs. The diagram below shows how a Centera integrates with CA DataMinder to work as an alternative object store.
Only events captured after integration has been set up will be migrated to EMC Centera. Events captured and replicated to the CMS before Centera integration has been set up will not be migrated to Centera. For this reason, we recommend that you set up Centera integration as soon as possible after deploying CA DataMinder.
For information on migrating existing events to a Centera, see How the Centera Integration Works. There is no inbuilt mechanism for migrating to Centera those blobs that were stored on the CMS before Centera integration was implemented. It is possible to do this, however. You will need to write a custom SQL procedure to add a blob queue record for each blob migrated to Centera..
Centera integration is configured through policy settings on the CMS. When a CA DataMinder event is captured or imported, it is replicated to the CMS. The CMS stores an event record in its database and writes a blob file to its \data subfolder. This blob file is subsequently moved to the Centera and the CMS database entry for that event is updated to reflect the new location for the blob.
Note: CA DataMinder uses version 3.1.544 of the Centera API Library to integrate with CentraStar. Integration is recommended with CentraStar 3.1. Integration may succeed with other versions but they may not have been tested. To find whether this version of the Centera API Library permits integration with other versions of CentraStar, please contact EMC Corporation.
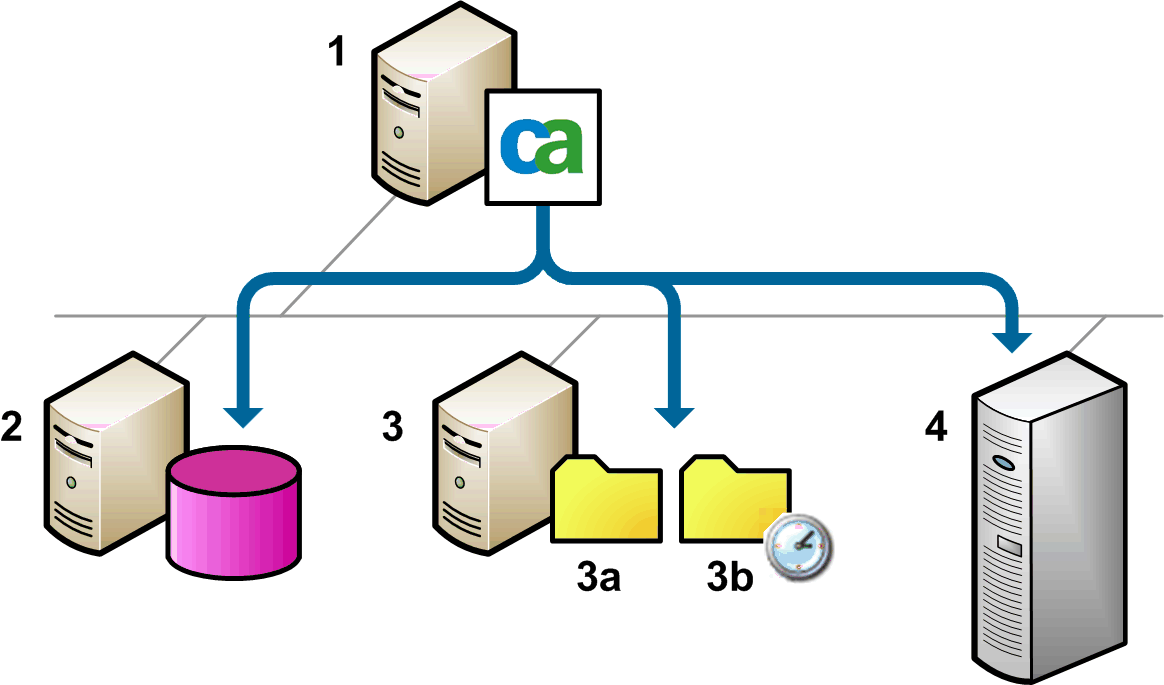
Centera architecture: Data flow
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|