

LCA는 CA ControlMinder 로컬 데이터베이스, 원격 데이터베이스 또는 PMDB를 업데이트하고 쿼리할 수 있습니다. 관리 API는 로컬 스테이션에서만 데이터베이스를 쿼리할 수 있습니다.
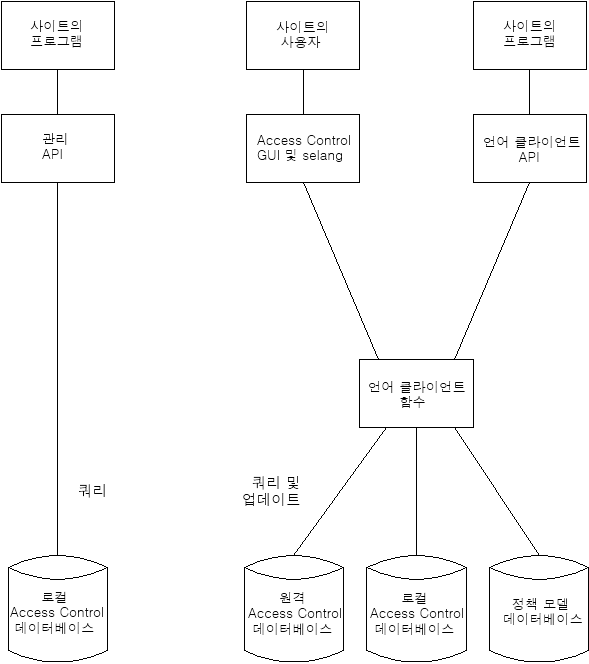
다음 다이어그램에서는 CA ControlMinder 데이터베이스의 레이아웃을 보여 줍니다.
다음 샘플 프로그램은 명령과 선택적으로 속성 이름의 목록을 명령줄 인수로 받습니다. 이 프로그램은 명령이 selang 명령이고 속성 이름은 dbmgr -d -r p ClassName 명령이 표시하는 형식(이전 버전의 CA ControlMinder에서는 rdbdump p 명령이 표시하는 형식)과 동일하게 표시되어야 한다고 가정합니다.
이 프로그램은 lca_ParseLine 함수를 호출하여 명령을 실행합니다. 실행 후 결과가 분석됩니다.
명령이 성공하면 쿼리 데이터를 처리하는 API 루틴이 호출되고 쿼리의 결과가 표시됩니다. 명령이 쿼리가 아닌 경우에는 쿼리 정보가 표시되지 않습니다. 속성의 목록이 제공된 경우 이러한 속성의 데이터만 표시됩니다. 명령이 실패하면 오류를 분석하는 API 루틴이 호출됩니다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <seostype.h>
#include <langapi.h>
static void scan_entities(void);
static void print_entity_info(LCA_QENT_H entity_handle);
static void scan_props(LCA_QENT_H entity_handle);
static void print_prop_info(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle);
static void scan_values(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle);
static void print_prop_value(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle,void *prop_value);
static char *Command = NULL;
static char **Properties = NULL;
static int NProps = 0;
static void put_commands(int argc,char **argv);
int ShowUsage(void)
{
fprintf( stderr, "Usage:\n
lca_examp Command [{List‑of‑property‑names}]\n");
return 1;
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
char *output = NULL;
int rv;
int n_ents;
char buff [1025];
/****************** Initialization ***********************/
/********************************************************/
if ( argc < 2 )
return ShowUsage();
rv = lca_Init("langapi",&output);
if ( rv )
{
printf( "Return value: 0x%08x\n"
"Msg: '%s'\n", rv, output );
return 1;
}
put_commands(‑‑argc,++argv);
/************** Execution of command **********************/
/********************************************************/
rv = lca_ParseLine(Command, &output);
/* print the command output */
printf("Command's output\n%s\n", output);
if (rv == 0)
{
/************ Success ‑ get the results *******************/
/********************************************************/
/** Get number of entities (objects) that were returned ***/
/********************************************************/
n_ents = lca_QEntsGetNum();
printf("number of entities returned: %d\n",n_ents);
/******* Get the names of the entities (objects) *********/
/********************************************************/
scan_entities();
}
else
{
/******************* The command failed ******************/
/********************************************************/
LCA_ERR_H error_handle = NULL;
/*********************************************************
* For further analysis of the error, review all errors
* (usually there is only one, but if there are warnings as
* well as errors, there could be more than one in the list).
*********************************************************/
printf("Numbers of errors: %d\n\n",lca_ErrsGetNum());
while ((error_handle = lca_ErrGetNext(error_handle))
!= 0)
{
printf("Severity: %d, Stage:%d\n",
lca_ErrSeverity(error_handle),
lca_ErrStage (error_handle));
rv = lca_Err2Str (error_handle, buff, sizeof (buff)‑1);
if ( rv )
printf ("Error message: '%s'\n", buff);
}
}
/************** Terminate the use of lca_ API **************/
/********************************************************/
lca_Terminate();
return 0;
}
static void put_commands(int argc,char **argv)
{
Command = argv[0];
Properties = ++argv;
NProps = ‑‑argc;
}
static void scan_entities(void)
{
LCA_QENT_H entity_handle = NULL;
while ( (entity_handle = lca_QEntGetNext(entity_handle)) != 0 )
print_entity_info(entity_handle);
}
/**************************************************************
Print the information for one entity, including its name, class name, and information about its properties.
If the entity is a class, the "name" will be empty, and the "class name" full.
If the entity is an object, the "name" will be full, and the "class name" empty.
*************************************************************/
static void print_entity_info(LCA_QENT_H entity_handle)
{
char *name;
if ( entity_handle == 0 )
return;
name = lca_QEntObjName(entity_handle);
if ( name != 0 )
printf("\nName: %s\t",name);
name = lca_QEntClassName(entity_handle);
if ( name != 0 )
printf("Class name: %s\n",name);
scan_props(entity_handle);
}
static void scan_props(LCA_QENT_H entity_handle)
{
LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle = NULL;
register int i;
if ( NProps == 0 )
while ( (prop_handle = lca_QPropGetNext(entity_handle,prop_handle)) != 0)
print_prop_info(prop_handle);
else
for ( i = 0; i < NProps; i++ )
{
prop_handle = lca_QPropGetByName(entity_handle,Properties[i]);
if ( prop_handle == 0 )
{
printf("Property %s does not exist for this entity.\n",
Properties[i]);
continue;
}
print_prop_info(prop_handle);
}
}
/*************************************************************
This function gets a property handle, and:
1. Gets its name and prints it.
2. Gets its value, translates it to a string, and prints it.
*************************************************************/
static void print_prop_info(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle)
{
char *prop_name = NULL;
char prop_type;
unsigned short prop_size;
unsigned int n_vals;
if ( prop_handle == 0 )
return;
prop_name = lca_QPropName(prop_handle);
if ( prop_name == 0 )
printf("Cannot get name of property. Handle: %d\n",
prop_handle);
printf("\nPropname: %s.",prop_name);
prop_type = lca_QPropType(prop_handle);
printf("Property type: %d; ",prop_type);
prop_size = lca_QPropSize(prop_handle);
printf("Property size: %d; ",prop_size);
n_vals = lca_QPropValsNum(prop_handle);
printf("Number of values: %d.\n",n_vals);
/* Loop over the property values, because there could be more
than one value for a property.
This happens if properties are of type list (ACLs, PACLs, User
list, Member list and so on).
*/
scan_values(prop_handle);
}
static void scan_values(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle)
{
void *prop_value;
int i;
int n_vals;
n_vals = lca_QPropValsNum(prop_handle);
for ( i=0; i<n_vals; i++)
{
prop_value = lca_QPropValGetByIdx(prop_handle,i);
print_prop_value(prop_handle,prop_value);
}
}
static void print_prop_value(LCA_QPROP_H prop_handle,void
*prop_value)
{
char buff[1024];
int n_vals;
if ( prop_handle == 0 || prop_value ==0 )
return;
n_vals= lca_QPropVal2Str(prop_handle,prop_value,buff,sizeof(buff));
if ( n_vals > 0 )
printf("Value: %s\n",buff);
}
LCA에는 다음 범주의 함수가 포함되어 있습니다.
langapi.h 파일에는 각 LCA 함수에 대한 기본적인 설명이 포함되어 있습니다. langapi.h 파일은 다음 디렉터리에 있습니다.
다음 함수는 LCA 작업을 제어합니다.
LCA를 초기화합니다.
특정 기능을 트리거하는 특정 통신 유형을 사용하여 LCA를 초기화합니다.
LCA를 종료합니다.
selang 명령을 수행합니다.
selang 명령을 수행하고 멀티바이트 형식 문자열을 입력할 수 있게 해 줍니다.
하나 이상의 호스트 목록에 연결합니다.
다음 함수는 LCA 암호를 제어합니다.
암호 규칙에 따라 새 암호를 검사합니다.
다음 함수는 오류에 대해 작동합니다. 오류는 실행 작업 함수에 의해 생성됩니다.
마지막으로 실행된 명령에 대한 오류 레코드 수를 반환합니다.
N번째 오류 레코드에 대한 LCA_ERR_H 유형의 오류 핸들을 반환합니다.
명령의 첫 번째 오류에 대한 LCA_ERR_H 유형의 오류 핸들을 반환합니다.
명령의 다음 오류에 대한 LCA_ERR_H 유형의 오류 핸들을 반환합니다.
오류의 주요 오류 코드를 반환합니다.
오류의 사소한 오류 코드를 반환합니다.
오류의 주요 오류 코드에 대한 정보 문자열을 반환합니다.
오류의 사소한 오류 코드에 대한 정보 문자열을 반환합니다.
오류의 심각도 수준을 반환합니다.
오류가 발생한 시기에 대한 정보를 반환합니다.
오류 레코드를 문자열 형식으로 변환한 후 버퍼에 복사합니다.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|