

There are thee general types of Metrics used for modeling the financial conditions of a service or contract. These are:
Consider the following example:
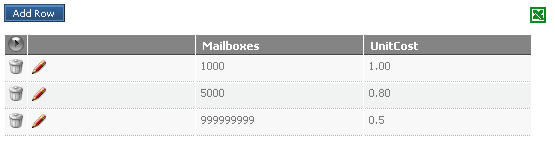
A new company is starting out and requires an Email service to be provided along with the setting up and maintenance of its mailboxes. As new staff are employed, the number of mailboxes will obviously increase. The provision of an Email Service for a Contract incurs a fixed price cost of $1000, plus there is an additional cost per mailbox that is to be charged per month. This cost per mailbox is a tiered pricing model as follows:
|
Number of Mailboxes |
Cost per Mailbox |
|
1-1,000 |
$1.00 |
|
1,001 - 5,000 |
$0.80 |
|
5,001+ |
$0.50 |
So, the more mailboxes that are added, the lower the additional cost. (For example: 1500 Mailboxes will cost (1000 x $1) + (500 x $0.80) = $1400.) Using this model, two Metrics can be produced to reflect this in the contract.
In addition there is an estimate by the management team of the number of staff members throughout the year (2007) as follows. The trend is due to initial company growth through employment and then from new offices opening in other regions:
|
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sept |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
50 |
100 |
500 |
900 |
1600 |
1700 |
1800 |
2500 |
2600 |
3500 |
3600 |
5800 |
To model these Metrics, do as follows:
Create the Fixed Cost Metric (use the Price Item type) in the contract, using the following details:
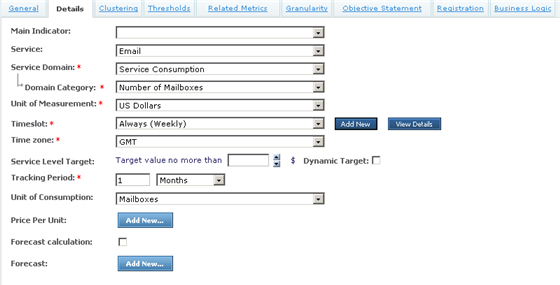
In order to specify the fixed cost to the Contract of this service, implement this as a Parameter to the Business Logic (where the fixed cost must be returned from the Result function) This parameter can then be exposed via the Objective Statement of the Metric, as shown below:
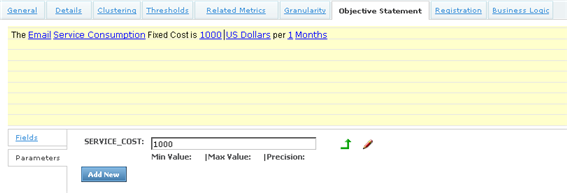
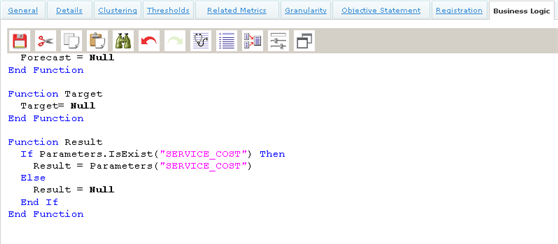
Returning the parameter value for this Metric, is simply a case of returning the value of the service cost via the Result function..
Next, create the variable pricing Metric (again, use Price Item Type) to determine the consumption costs of the number of mailboxes used. Name this Metric 'Mailbox Consumption Cost' and create it with the following details:
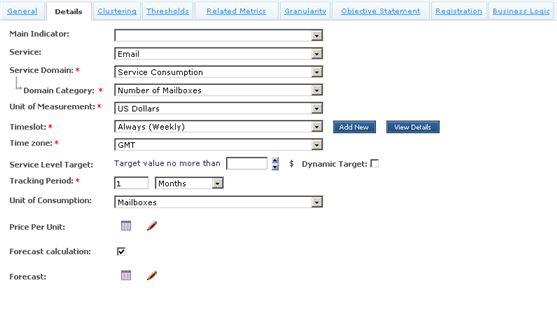
In this instance, you need to enter the consumption parameters into the Metric details. These will go into the Price Per Unit table. To model the table above for the number of mailboxes against the cost, create a column for the upper limit of mailboxes and one of the unit prices:
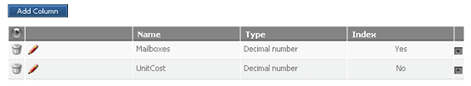
Then enter the values for each tier. In this case, the upper limit of mailboxes determines the cost bracket associated with it. Since there are 3 tiers, they are added to the table in this manner:
In addition to this, implement the forecasting function on the consumption of Mailboxes. Do this by creating the Forecast table with the preset Monthly layout.
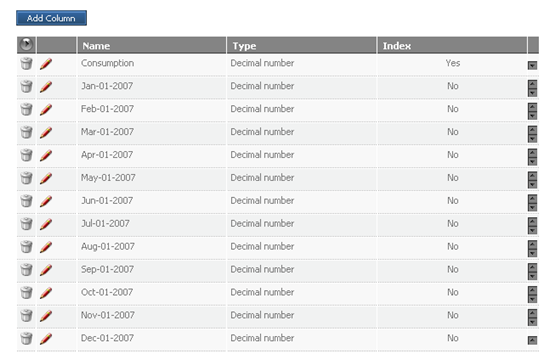
This is then filled with the values from the tables given in the scenario description.
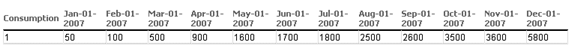
Now you can add the Objective statement for the Metric. In this case, no parameter values are required since they are derived from the 'Price Per Unit' and 'Forecast' tables.
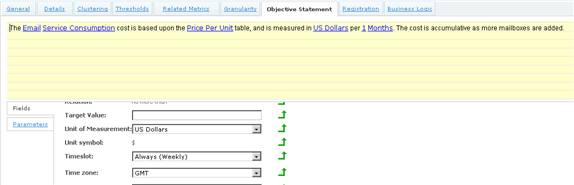
Finally, complete the Business Logic as follows:
Option Explicit
Dim PPUmap1, PPUmap2, PPUmap3, PPUkey, FCmap, periodFC, TierPPU
Dim currentMonth, TotalMailboxes, MailboxesThisPeriod, TotalPrice
Sub OnRegistration(dispatcher)
'sample registration only
dispatcher.RegisterByMetric "OnMailboxAddedEvent", "NewMailboxEventType", _
"MailboxResource", "MONTH", "MetricName", "MetricContract", _
"MetricContractParty"
End Sub
Sub OnLoad(TIME)
'Initialise the price tier maps and forecast maps
Set PPUmap1 = Context.Field ("Price Per Unit")(1)
Set PPUmap2 = Context.Field ("Price Per Unit")(2)
Set PPUmap3 = Context.Field ("Price Per Unit")(3)
Set FCmap = Context.Field ("Forecast")(1)
End Sub
Sub OnPeriodStart(TIME)
'TODO: ADD code here TO handle period START event
currentMonth = GetMonth (time)
If Context.IsInForecast Then
periodFC = getForecastValue (currentMonth)
End If
MailboxesThisPeriod = 0
TotalPrice = 0
End Sub
Sub OnPeriodEnd(TIME, isComplete)
' Calculate the current price of all the mailboxes using the tiered
' pricing model
' This uses a cumulative approach as it goes through each tier to
' determine total cost.
TotalPrice = getMailboxCost (TotalMailboxes)
End Sub
Sub OnTimeslotEnter(TIME)
End Sub
Sub OnTimeslotExit(TIME)
End Sub
Sub OnMailboxAddedEvent(eventDetails)
MailboxesThisPeriod = MailboxesThisPeriod + 1
TotalMailboxes = TotalMailBoxes + 1
End Sub
Function Forecast
Forecast = getMailboxCost (periodFC)
End Function
Function Target
Target = Null
End Function
Function Result
result = TotalPrice
End Function
Function getforecastvalue(q)
getforecastvalue = FCmap (q)
End Function
Function getmonth(time)
'this function retrieves the month
Dim lTime
lTime = Tools.GetLocaleTime(time)
getmonth = monthname (datepart ("m", lTime), True) & _
"-0" & datepart ("d", lTime) & "-" & datepart ("yyyy", lTime)
End Function
Function getMailboxCost(num_boxes)
'Function calculates the cost of the mailboxes using the tiered pricing model
Dim returnValue
If num_boxes <= PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes") Then
'First tier
returnValue = num_boxes * PPUmap1 ("UnitCost")
'Out.Log "Tier1: " & num_boxes
Else If num_boxes > PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes") And num_boxes <= PPUmap2 ("Mailboxes") Then
'second tier only
returnValue = (PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes") * PPUmap1 ("UnitCost")) + _
((num_boxes - PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes")) * PPUmap2 ("UnitCost"))
'Out.Log "Tier2: " & num_boxes
Else If num_boxes > PPUmap2 ("Mailboxes") Then
'third tier
returnValue = (PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes") * PPUmap1 ("UnitCost")) + _
((PPUmap2 ("Mailboxes") - PPUmap1 ("Mailboxes")) * PPUmap2 ("UnitCost")) + _
((num_boxes - PPUmap2 ("Mailboxes")) * PPUmap3 ("UnitCost"))
'Out.Log "Tier3: " & num_boxes
End If
getMailboxCost = returnValue
'Out.Log "Cost is: " & returnValue
End Function
Note: This Business Logic script handles both the forecast calculation (using the 'Forecast' table) and the Financial Consumption Cost results. Both use of the same formula getMailboxCost() which calculates the tiered pricing based upon the 'Price per Unit' table defined for this Metric.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|