

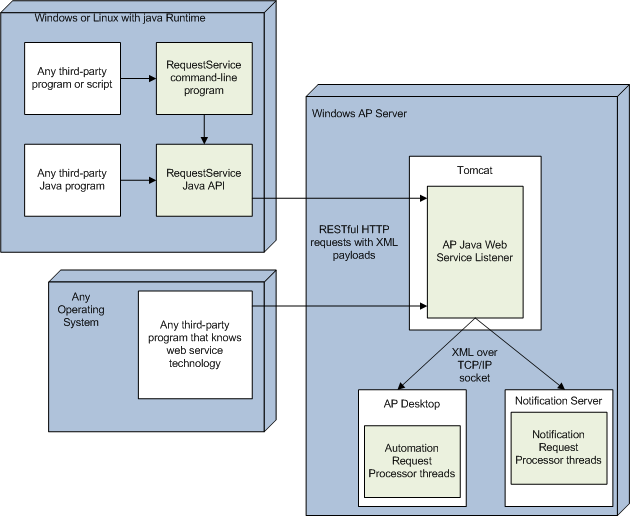
The AP Web Service Listener is a Java application that accepts web service requests from clients and returns replies to those clients. The Listener is bundled into a web application archive (or .WAR file) and deployed under Tomcat. The Listener must be running for the AP web services to be operational.
Once the AP Web Service Listener is deployed, you can write application software to issue HTTP methods to the appropriate URI. By sending HTTP methods with attached XML documents, applications can talk directly to the AP server from any computer in your corporate network.
The Listener dispatches the requests that it receives to the appropriate AP component to perform the desired operation for the calling program. The two AP components that perform the actual operations are the Automation Request Processor (AP Desktop) and the Notification Request Processor (Notification Server).
This term represents the threads and logic within the AP Desktop application that perform the desired web service operations that are related to automation. This term includes, operations on messages and operations on sessions.
This term represents the threads and logic within the Notification Server that perform the desired web service operations that are related to notifications. This term includes, send, answer, and query a notification.
You are not required to use any CA client software to communicate to the AP web services. From many different programming languages, you can issue HTTP requests against specific URIs and can process their replies.
However, if you are the programmer of a Java application you likely already have the expertise to invoke Java methods. You may not have the expertise (or inclination) to perform web service communications. The RequestService Java API performs all of the communications necessary to transmit requests and receive replies from the AP web service. Use of the Java API can shorten the time that is required for you to integrate your Java application with CA Automation Point.
Engineering staff often perform their integration work using command line tools and scripting languages. The requirement to write a complete application program that correctly uses the HTTP protocol can sometimes be more time consuming than an organization can afford. We provide an optional command-line client application that is called RequestService to reduce programming effort and to reduce the requirement to understand fully the HTTP protocol.
The RequestService application has the following capabilities:
Behind the scenes, the RequestService command-line application utilizes the RequestService Java API to perform most of its functionality. A Java Runtime Environment (JRE) must be installed before you can use the RequestService application.
The RequestService command-line application is less flexible in processing XML replies than the RequestService Java API. However, the RequestService command-line application provides an easy on-ramp for integrating a third-party application to CA Automation Point through web services with minimal programming.
The following diagram shows how the AP web service components are deployed.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|