

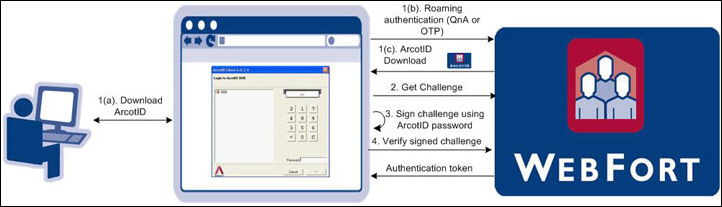
Authentication using CA AuthID is a PKI-based challenge-response mechanism. The client obtains an authentication token by proving the private key of the user. The client-server interactions during authentication are as follows:
Your application or the resource that is protected by Strong Authentication obtains the user credentials. For example, if the user’s CA AuthID is not available on the system or the USB.
Your application requests for a challenge used to authenticate the user.
Strong Authentication Server prepares a unique challenge and sends it to your application.
The user enters the correct CA AuthID password to uncover the CA AuthID. The client signs this challenge with the user’s private key that is available as a result of uncover. The challenge can either be pre-loaded on the client machine or can be downloaded from the server.
The signed challenge is sent to the Strong Authentication Server for verification. If the signature is verified successfully, the user can login or access your protected resource. For every successful transaction, Strong Authentication also returns an authentication token for a user.
The following figure illustrates the CA AuthID authentication flow.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|