

An increase in the NRTT and in the Observations count is a strong indicator that a performance problem is based on an application utilization of the network. The strength of this indicator can be reinforced by correlating it with other corresponding data points to build a complete finding that the problem source is the network.
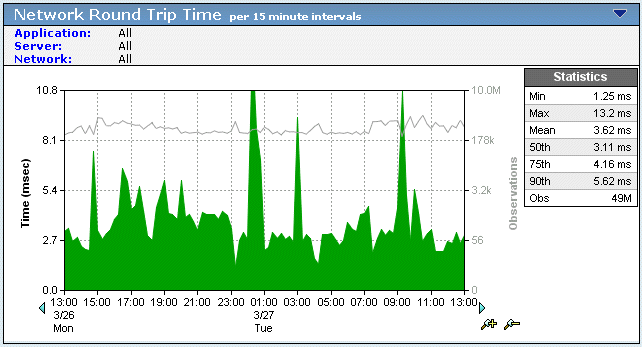
If both the NRTT and number of Observations peak at the same point in time as the observed performance issue, review the following data sets for the same point in time:
Check whether the length of retransmissions increased. Retransmissions indicate that network queues are filling at a rate faster than they can be emptied, thus incurring packet drop and related TCP retransmissions
Check whether there is a concurrent increase in Network Connection Setup Time. This increase indicates the three-way TCP handshake is being delayed on the network because of queue depth being increased by other pre-established sessions within the network.
Check whether the number of TCP/IP sessions increased by a significant number (greater than 10%). Additional TCP sessions and accompanying application data require more bandwidth.
Check whether the Data Volumes/Rates increased. Higher volumes of data on the network increase queue depth and related delay. Abnormal increases in data volumes that coincide with increases in NRTT indicate a network having difficulty keeping up with demand.
Check whether there is a significant increase in the number of users. Increases in network utilization typically coincide with increases in numbers of users. The point at which a certain number of users cause the NRTT to degrade can be interpreted as a future proactive point for upgrading network bandwidth for other similar sites.
Check whether there was an increase in the standard deviation for NRTT and/or Percentiles. This increase indicates inconsistent and sporadic performance by the network as evidenced in more "outlying" data points (such as, points that are at significantly varying distances from the average), and is a strong indicator of network based issues.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|