

|
At a Glance |
|
|
Catalog |
system_ms |
|
Category |
Database Appliances |
|
User volumes |
yes |
|
Min. memory |
512 MB (SQL08X/WG), 1G (SQL08D/W/S/E) |
|
OS |
Windows |
|
Constraints |
no |
|
Questions/Comments |
|
SQL08y_0N is a database appliance based on Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (http://www.microsoft.com/sqlserver/). It provides an easy way to add a Microsoft SQL database to any application.
SQL08y_0N stores the database on an application-defined volume configured on each SQL08y instance. The SQL08y database volume cannot be shared among multiple SQL08y instances.
SQL08y_0N clients access the configured database through the in terminal. The database requests are processed and completed back through the same terminal. SQL08y allows any valid user to access the database through the in terminal (the appliance has one pre-configured superuser role: standard 'sa'). SQL08y can be configured with the maximum number of concurrent connections supported through in.
The appliance connected to SQL08y is responsible for creating its own database and tables if they do not exist. Alternatively, an initial database can be manually copied to the data volume.
SQL08y_0N stores its logs internally in its database.
Important! SQL08y_0N is not distributed with CA AppLogic. See the installation reference for instructions on creating SQL08y_0N from a base windows server appliance.
|
Name |
Latest Version |
OS |
SQL Server |
Notes |
|
SQL08X_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Standard Edition R2 (32-bit) |
SQL 2008 Express with Advanced Services (x86) |
|
|
SQL08WG_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Standard Edition R2 (32-bit) |
SQL 2008 Workgroup (x86) |
|
|
SQL08D_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Developer (x64) |
|
|
SQL08W_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Web (x64) |
|
|
SQL08S_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Standard (x64) |
|
|
SQL08E_03 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2003 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Enterprise (x64) |
|
|
SQL08X_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Standard Edition without Hyper-V SP2 (32-bit) |
SQL 2008 Express R2 (x86) |
|
|
SQL08WG_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Standard Edition without Hyper-V SP2 (32-bit) |
SQL 2008 Workgroup R2 (x86) |
|
|
SQL08DC_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Datacenter R2 (x64) |
|
|
SQL08W_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Web R2 (x64) |
|
|
SQL08S_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Standard R2 (x64) |
|
|
SQL08E_08 |
1.1.1-1 |
Windows 2008 Datacenter Edition R2 (64-bit) |
SQL 2008 Enterprise R2 (x64) |
|
SQL08Y 03
Express/Workgroup (x86)
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
Tested |
|
CPU |
0.1 |
4 |
0.25 |
4 |
|
Memory |
512 MB |
4 GB |
1 GB |
4 GB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
100 Mbps |
2 Gbps
|
Developer/Web/Standard/Enterprise (x64)
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
Tested |
|
CPU |
0.25 |
32 |
0.5 |
8 |
|
Memory |
1 GB |
64 GB |
1 GB |
32 GB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
100 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
SQL08Y 08
Express/Workgroup (x86)
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.25 |
4 |
0.5 |
|
Memory |
768 MB |
4 GB |
1 GB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
100 Mbps |
Datacenter/Web/Standard/Enterprise (x64)
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.25 |
32 |
0.5 |
|
Memory |
1 GB |
64 GB |
1 GB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
100 Mbps |
Note: Memory should be increased based on two main factors: number of concurrent users and database size. Typically, SQL08y_09 can support about 50 concurrent users per 1G of memory. The larger the database, the more memory SQL08y_09 should have for processing. For example, SQL08y_09 should be configured with at least 1G of memory for a 10G database - more than 1G for better performance.
|
Name |
Direction |
Protocol |
Description |
|
in |
in |
Any |
Receives MSSQL database requests from clients. |
|
mon |
out |
CCE |
Sends performance and resource usage statistics. This terminal may be left unconnected. |
The default interface is enabled. It is intended for diagnostics and troubleshooting (over SSH). Future versions of this appliance may disable SSH access.
|
Volume |
Description |
|
data |
Volume for the database data storage. |
Important: The data volume must exclusively dedicated to the SQL08y_09 instance (it cannot be shared with other appliances).The data volume for appliances based on Windows Server 2003 should be minimum 1GB of type ntfs03 and be at least 1 GB in size, while the data volume for appliances based on Windows Server 2008 should be of type ntfs08 and be at least 3 GB in size
Note: None of the SQL08y_0N properties are case sensitive excluding file names and paths.
|
Property Name |
Type |
Description |
|
read_only |
String |
Whether the database defined in user_db_name and accessed through the in terminal is read-only. Possible values are on for read-only and off for read/write. This property is used by SQL08y_0N only to optimize performance for the database (read-only databases do not need garbage collection, and so on). |
|
sa_password |
String |
Administrator sa account password. manager if empty. |
|
user_db_name |
String |
Default user database (user_login option has to be defined). |
|
user_login |
String |
Database user account name. |
|
user_password |
String |
Database user password. |
|
max_connections |
Integer |
The maximum number of concurrently active connections to the database that SQL08y_09 should handle through the in terminal. SQL08y_09 uses this value in advanced calculations for memory management. In general, SQL08y_09 needs 1G of memory for every 50 concurrent connections. Once the connection limit is reached, SQL08y_09 refuses all subsequent connections. If set to 0 - SQL08y_09 will automatically manage a connection pool limits. |
The SQL08y_09 appliance reports the following custom counters through the mon terminal. These counters belong to the SQL08y_09 counter group:
|
Counter Name |
Description |
|
Current connections |
Current number of client connections established |
|
Memory usage |
Memory usage of the server process |
|
Lock requests/sec |
Number of lock requests per second |
|
Lock waits/sec |
Number of lock waits per second. These are lock requests that could not be given immediate lock grants and were put in a wait state |
|
Deadlocks/sec |
Number of lock requests per second that resulted in a deadlocks |
|
Active transactions |
Total number of active update transactions for all databases |
Important! The counter's pace in the appliance is set to 10s. If you are using graphs via the MON appliance to monitor these counters, the pace for the graphs need to be set to 10s or multiple of 10s.
SQL08y_09 can be debugged through the standard Profiler, and though the in interface. This is useful for tracking SQL statements, seeing how long it takes to execute SQL statements, seeing why an SQL statement is failing, and so on. The debug information includes:
The debug information is stored in the SQL08y_09 logs and is available through MSSQL statistic views/stored procedures.
The following diagram shows a typical usage of the SQL08y_09 appliance in a two-tier web application geared toward a lot of users executing simple queries:
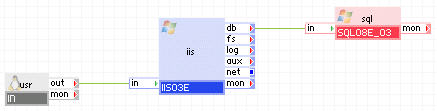
Appliances in use:
Client requests arrive on the usr gateway. The gateway forwards the requests to the iis server, which serves the request. When script (for example, ASP.NET or ASP) on iis need to access persistent data, it uses the sql appliance through the db terminal.
In this example, the database used with sql is not read-only and many users may access it through iis executing simple queries.
Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
read_only |
no |
Database is not read-only, it may be modified. |
|
max_connections |
0 |
Manage memory settings automatically. |
|
sa_password |
manager |
Default password. |
|
user_db_name |
web |
Default database for user 'website'. |
|
user_login |
website |
Database user account. |
|
user_password |
pa$$word |
Database password. |
Note: The data volume must also be configured on sql and the content volume must be configured on iis. To create application volumes that can be used here, see the User Volumes topic.
The following diagram shows a typical usage of the SQL08y_0N appliance in a two-tier web application in which the database is used to share state and data between multiple, load-balanced web servers (geared toward a lot of users executing simple queries). In addition, this example has a separate input for maintenance, through which an administrator can log in and access the database for maintenance and an input through which an administrator can read the MSSQL logs.
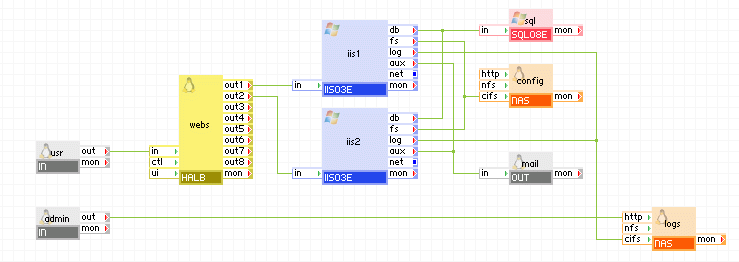
Appliances in use:
Client requests arrive on the usr gateway. The gateway forwards the requests to the webs load balancer, which directs the request to one of the web servers ( iis1 or iis2). When scripts (for example, ASP.NET) on the web servers need to access persistent data, they use the sql appliance through their db terminals.
Administrator can log in through the admin gateway to the logs appliance and view the web server logs.
In this example, the database used with sql is not read-only and many users may access it through the web servers executing simple queries. Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
read_only |
no |
Database is not read-only, it may be modified. |
|
max_connections |
10 |
Maximum 10 simultaneous connections. |
|
sa_password |
manager |
Default password. |
|
user_db_name |
iis |
Default database for user 'website'. |
|
user_login |
website |
Database user account. |
|
user_password |
pa$$word |
Database password. |
Note:
The following diagram shows a typical usage of the SQL08y appliance in a two-tier web application implementing a decision-support system for a few users executing complex queries over a large database that is several GBs in size.
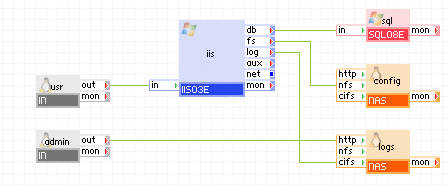
Appliances in use:
Client requests arrive on the usr gateway. The gateway forwards the requests to the iis server, which serves the request. When scripts (for example, ASP.NET) on iis need to access persistent data, it uses the sql appliance through the db terminal.
Using a browser, administrators connect to the admin gateway to view web logs. The admin gateway forwards the requests to the logs NAS appliance.
In this example, the database used with sql is not read-only and users may access it through iis executing complex queries.
Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
max_connections |
25 |
Database is limited to 25 concurrent users. |
|
read_only |
no |
Database is not read-only, it may be modified. |
|
sa_password |
manager |
Default password. |
|
user_db_name |
web |
Default database for user 'website'. |
|
user_login |
website |
Database user account. |
|
user_password |
pa$$word |
Database password. |
Note: The data volume must also be configured on the sql appliance and the data volume must also be configured on the logs appliance.
A less common usage of the SQL08y_0N appliance is a two-tier web application using a read-only database. In this case, SQL08x_0N in the previous simple application examples can be parameterized to use a read-only database (no modifications are allowed) by setting the read_only property to yes. This will disable various MSSQL features that are not needed for read-only databases which results in better performance. Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
read_only |
yes |
Database is read-only, modifications are not allowed. |
|
max_connections |
0 |
Manage memory settings automatically. |
|
sa_password |
manager |
Default password. |
|
user_db_name |
empty |
Default. |
|
user_login |
empty |
Default. |
|
user_password |
empty |
Default. |
The appliance hostname (set to appliance instance name) cannot be longer than 15 characters. Setting the appliance instance name to more than 15 characters will result in a hostname truncated to the 15th character.
Note:
SQL08y_0N uses the following 3rd party open source packages in addition to the 3rd party open source packages used by its base class WIN03x.
|
Software |
Version |
Modified |
License |
Notes |
|
php |
5.2.10 |
No |
PHP License v3.01 |
N/A |
|
Microsoft SQL Driver for PHP |
1.1 |
No |
Ms-PL |
N/A |
|
dotnetfx |
3.5 SP1 |
No |
online EULA |
free Microsoft download (.NET framework) |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB942288 |
v4 |
No |
online EULA |
free Microsoft download (support hotfix) |
|
SQL Server Express with Advanced Services |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Freeware, SQL Server 2008 Redistribution EULA |
free Microsoft download |
|
SQL Server Web Edition |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Commercial |
"Per Processor" or "Server plus Device CALs" or "Server plus User CALs" |
|
SQL Server Workgroup Edition |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Commercial |
"Per Processor" or "Server plus Device CALs" or "Server plus User CALs" |
|
SQL Server Developer Edition |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Commercial |
"Per Developer"; must be used for designing, developing, and testing purposes only |
|
SQL Server Standard Edition |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Commercial |
"Per Processor" or "Server plus Device CALs" or "Server plus User CALs" |
|
SQL Server Enterprise Edition |
2008 SP1 |
No |
Commercial |
"Per Processor" or "Server plus Device CALs" or "Server plus User CALs" |
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|