

Catalogs are an easy way to package multiple appliance classes into a library. A catalog can be used in multiple applications, or it may contain appliances that are used in a single large application.
Each appliance class consists of a class descriptor and one or more class volume images referenced by that descriptor. Each assembly class consists of a class descriptor similar to the class descriptor of the regular appliance classes, and an interior descriptor that captures the structure inside the assembly.
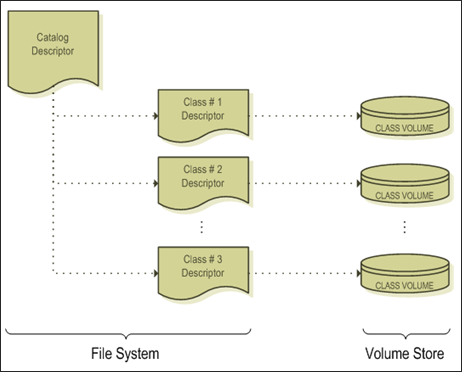
A catalog consists of a catalog descriptor that lists all classes included in the catalog, and a set of class descriptors. Each class descriptor, in turn, refers to one or more class volumes or interior descriptors.
Catalogs are implemented as shared directories, in which all descriptors reside. The associated volumes may reside in the same directory (as volume image files), or in the volume store.
Tip: Placing the volume images in files makes it easy to publish a catalog through a web or ftp interface.
The name of a class included in a catalog is unique within the catalog. When a class makes a reference to another class contained within the same catalog, the name of that class is sufficient to resolve the reference. Whenever a class has a reference to a class from another catalog, the name of the catalog is pre-pended to the name of the class to form a name that is unique in the class name space.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|