

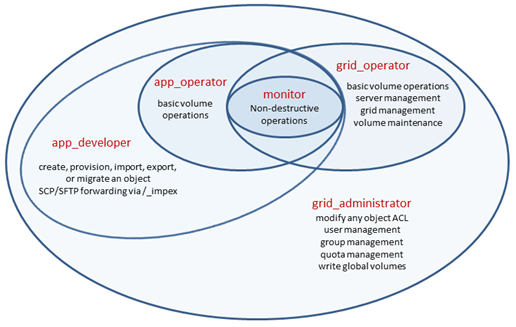
The following diagram provides a visual representation of the relationships among the grid object access levels:
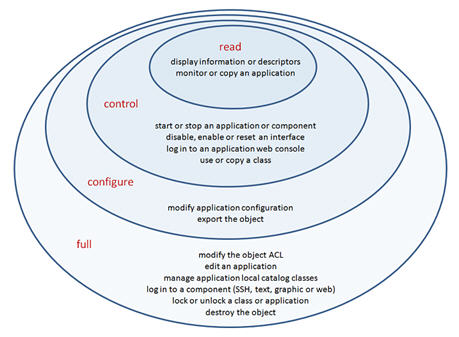
The following diagram provides a visual representation of the relationships among the application and global catalog access levels:
The following table indicates in detail what operations are permitted according to the grid access level provided to the executing user.
|
|
Grid Operations |
monitor |
app_operator |
app_developer |
grid_operator |
grid_administrator |
|
Application Mgmt. |
list applications |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
migrate an application3 or class4 |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
provision an application6 |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
create or import an application |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
Catalog Mgmt. |
list catalogs |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
migrate a catalog5 or class4 |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
create a global catalog |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
Grid Management |
display or list dashboard messages |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
display controller system log messages |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
display grid high availability information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
display grid information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
list servers |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
display server information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
SCP/SFTP forwarding via /_impex |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
display the grid ACL |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
mark or reset the controller system log |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
create, destroy or modify a dashboard message |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
set, power cycle, reboot or shutdown the grid |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
check grid high availability |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
set, disable, enable, identify, power cycle, power off, power on, reboot or shutdown a server |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
display or modify the ACL of any object |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
User/Group/Quota Management |
user log in |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
list users/groups/quotas |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
display user/group/quota information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
create or destroy a user |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
unlock any user2 |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
set any user profile properties2 |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
create or modify quotas |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
create, destroy or modify a group |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
Volume Management |
list volumes |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
display volume information1 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
display volume repair status |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
create, destroy, format, rename or resize a volume7 |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
copy a volume8 |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
set, manage, fscheck or fsrepair a volume10 |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
import or export a volume9 |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
check, clean, migrate or repair volumes |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
write operations on global volumes |
|
|
|
|
X |
1 Getting information about an application user volume, application local catalog class volume or singleton volume requires at least read access level rights on the application. Getting information about a global catalog class volume requires at least read access level rights on the catalog.
2 Providing they can log in, any user can unlock their own user account, and any user can set their own user profile properties.
3 Migrating an application --export requires full access level rights on the application.
4 Migrating a global catalog class --import requires full access level rights on the global catalog. Migrating an application local catalog class or singleton --import requires full access level rights on the application. Migrating a global catalog class --export requires configure or full access level rights on the global catalog. Migrating an application local catalog class or singleton --export requires configure or full access level rights on the application.
5 Migrating an application local catalog --import requires full access level rights on the application. Migrating an application local catalog --export requires configure or full access level rights on the application. Migrating a global catalog --export requires configure or full access level rights on the catalog.
6 Provisioning an application requires at least read access level rights on the application. Provisioning a filer system application is a special case and is not limited to application developers and grid administrators.
7 These volume operations require full access level rights on the application if the volume is an application user or singleton class volume. Creating a symlink to an application user volume also requires full access level rights on the linked application. Write operations on global volumes require grid_administrator access level rights.
8 When copying a volume, if the source volume is a global catalog class volume then at least control access level rights are required on the catalog. If the source volume is an application user volume or an application local catalog class volume or an application singleton volume, then at least read access level rights are required on the application. If the destination volume is an application user volume or an application singleton volume, then full access level rights are required on the application.
9 Importing an application user volume or a singleton class volume requires full access level rights on the application. Exporting an application user volume or an application singleton volume requires configure or full access level rights on the application.
10 If the volume is an application user volume or an application local catalog class volume or a singleton volume then full access level rights are required on the application. If the volume is a global catalog class volume then configure or full access level rights are required on the catalog.
A grid administrator does not have the implicit right to modify or destroy an application or global catalog; however, a grid administrator can grant himself such rights by modifying the object ACL.
Users with grid_administrator access can set the owner to anyone. Users with all other accesses can set the owner only to themselves or a group that they are a member of.
Note: Ensure that any group that you define as an owner has the can_own attribute.
The following table indicates in detail what operations are permitted according to the application access level provided to the executing user.
|
Application Operations |
read |
control |
configure |
full |
|
monitor the application |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
display the application configuration |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
display the application, component or iface information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
get the application package descriptor |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
copy the application4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
log in to the application web console |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
start, stop, build, clean, continue, repair or restart the application3 |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
disable, enable or reset a component iface |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
start, stop, continue or restart a component |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
export the application2 |
|
|
X |
X |
|
modify the application configuration |
|
|
X |
X |
|
edit the application in the GUI editor |
|
|
|
X |
|
create, destroy branch, copy or move an application local catalog class5 |
|
|
|
X |
|
SCP forwarding to via /app to a running appliance1 |
|
|
|
X |
|
log in to an appliance (SSH, text, graphic or web) |
|
|
|
X |
|
lock or unlock the application |
|
|
|
X |
|
rename or destroy the application |
|
|
|
X |
|
display or modify the application ACL |
|
|
|
X |
|
configure the application in the GUI editor Note: When a user attempts to edit an application for which they have “configure”, but not “full” access, the GUI editor is opened in config-only mode. In config-only mode, the user can configure the application, but they cannot change its definition. |
|
|
X |
X |
|
view the application in the GUI editor Note: When a user attempts to edit an application for which they have "read" or "control" access, but not "configure" or "full" access, the GUI editor is opened in read-only mode. A user cannot change the definition or configuration of an application in "read-only" mode. |
X |
X |
X |
X |
1 Requires the user to have app_operator, app_developer or grid_administrator access level rights on the grid.
2 Importing or exporting an application or a global catalog or global catalog class requires app_developer or grid_administrator access level rights on the grid.
3 Except for the stop and clean operations, all of these operations require at least control access level rights on the catalog for each referenced global catalog class in the application.
4 Copying an application requires app_developer or grid_administrator access level rights on the grid.
5 When copying or moving a class, if the source class is an application singleton or application local catalog class, or the destination class is an application singleton or application local catalog class, then full access level rights are required on the application. If the source class is a global catalog class, then at least control access level rights are required on the catalog. If the destination class is a global catalog class then full access level rights are required on the catalog.
The following table indicates in detail what operations are permitted according to the catalog access level provided to the executing user.
|
Catalog Operations |
read |
control |
configure |
full |
|
display class information |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
get a class descriptor |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
use a class |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
copy a class1 |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
branch a class2 |
|
|
X |
X |
|
export the catalog or class3 |
|
|
X |
X |
|
create, destroy or rename a class |
|
|
|
X |
|
lock or unlock a class |
|
|
|
X |
|
destroy the catalog |
|
|
|
X |
|
display or modify the catalog ACL |
|
|
|
X |
If the source class is an application singleton or application local catalog class, or the destination class is an application singleton or application local catalog class, then full access level rights are required on the application. If the source class is a global catalog class, then at least control access level rights are required on the catalog. If the destination class is a global catalog class then full access level rights are required on the catalog.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|