

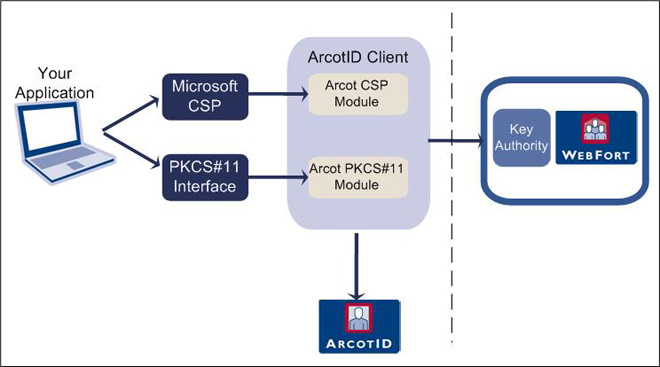
In addition to providing strong authentication, CA Auth ID can also be used as a secure container to store digital certificates and private keys that can be used for different applications or operations such as, email signing (S/MIME), document signing, certificate-based authentication (open PKI). This process of managing private key storage in the CA Auth ID is performed by Key Authority (KA).
An unsigned attribute is created in the CA Auth ID to store these credentials and this attribute is referred to as Key Bag or Key Vault. The digital certificates are stored in an unencrypted format in the Key Bag, but the private keys are encrypted using a key called Key Authority key, which is stored in the CA Strong Authentication database.
To use the private keys that are stored in a Key Bag, the CA Auth ID Client (see "CA Auth ID Client") makes a request for the KA key to CA Strong Authentication Server by signing the request with the user’s private key. The CA Strong Authentication Server authenticates the incoming request and sends the KA key to the client, which then uses this key to open the Key Bag and access the private keys.
The following figure illustrates how to use CA Auth ID as an open PKI container.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|