

Latest version: 2.0.1-1
|
At a Glance |
|
|
Catalog |
System |
|
Category |
Web Servers |
|
User volumes |
yes |
|
Min. memory |
736 MB |
|
OS |
Linux |
|
Constraints |
no |
|
Questions/Comments |
|
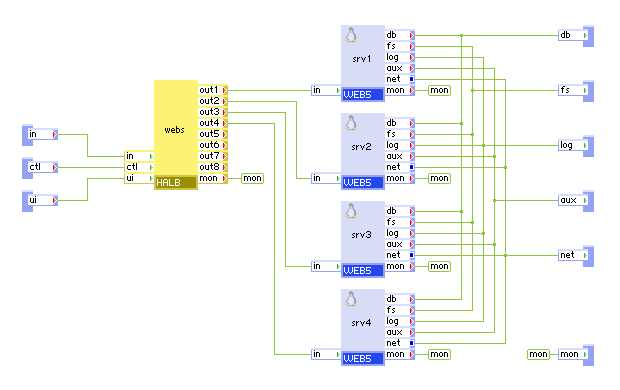
WEBx4 is a scalable web server that consists of a single load balancer (HLB) and four web servers (WEB5).
WEBx4 serves static web content and executes scripts from a user-configurable read-only content volume. The paths to the documents and scripts are configurable, so that the same volume can be shared between multiple web servers and/or other appliances serving different content.
WEBx4 has three generic output terminals intended for accessing external services from scripts on the content volume. The db terminal is for accessing a MySQL database; the fs terminal is for accessing shared file storage (using NFS); and the aux terminal is for sending e-mail messages to an SMTP server.
The log terminal can be used to connect WEBx4 to a shared file system on which WEBx4 can store its logs.
The configuration of the web server is provided through properties. The properties are designed to cover the most uses in an easy-to-configure way and in most cases only a few need to be set to non-default values. Advanced configurations can be achieved through include files in the Apache configuration format, coming from the content volume. Access and options to content and script files can be further specialized through .htaccess files in the content directories.
If the features provided by the WEBx4 appliance do not meet your needs, please contact our Technical Support to discuss the possible options. We may be able to extend the catalog by providing appliances that cover your needs.
Resources
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.5 |
80 |
0.6 |
|
Memory |
768 MB |
160 GB |
800 MB |
|
Bandwidth |
5 Mbps |
10 Gbps |
800 Mbps |
Terminals
|
Name |
Dir |
Protocol |
Description |
|
in |
in |
http |
Serves HTTP requests coming from web clients. Serves the HTTP/1.1 and 1.0 protocols. |
|
ctl |
in |
http |
Control terminal that is used for enabling/disabling the outputs and retrieving output terminal state from load-balancer. |
|
ui |
in |
http |
Exposes a Web UI that contains load-balancer runtime statistics. |
|
db |
out |
mysql |
Access to a MySQL server. Usage is defined by whatever scripts reside on the content volume (if any). This terminal may be left unconnected if it is not used. |
|
fs |
out |
nfs |
Access to a network file system for shared file storage, providing read-write file access over NFS. Usage is defined by whatever scripts reside on the content volume (if any). Software on the content volume sees the mounted remote file system as /mnt/fs in the appliance's filesystem space. This terminal may be left unconnected if it is not used. The connected server must have a read-write share named /mnt/data. |
|
log |
out |
cifs |
Access to a CIFS-based network file system for storing access and error logs. This terminal may be left unconnected if it is not used. The connected server must allow anonymous logins and have a read-write share named share. |
|
aux |
out |
any |
Access to an SMTP server for sending outgoing e-mail. Usage is defined by whatever scripts reside on the content volume (if any). Note that 'sendmail' is not configured on the appliance, any application that needs to send mail, should simply use SMTP directly, using 'aux' as the target hostname. For Perl CGI scripts the Mail::Mailer module can be used to do that. |
|
net |
out |
any |
Gateway output for subnet access. |
|
mon |
out |
cce |
Sends performance and resource usage statistics. |
User Volumes
|
Volume |
Description |
|
content |
Read-only, shareable volume providing the web content (documents, media and scripts) to be served by WEBx4. |
The volume may provide static and/or dynamic content with an optional configurable directory dedicated for scripts. Script execution from any directory can also be configured using a file name pattern.
In addition to content, the document directory (configured through the docs_dir property) on the content volume may also hold the following optional configuration files, all in the standard Apache configuration format (see http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.0):
.htaccess - Per-directory configuration. Each directory may have its own .htaccess file, defining options and access rules for the files in that directory and its sub-directories. The use of .htaccess files is disabled by default. Because the content volume is read-only and is not typically modified at runtime, it may be better to configure per-directory access using Directory or Location sections in the custom config files in the .apache_conf directory (see above). Enable the use of .htaccess with the use_htaccess property, if the use of config files is not feasible or if some of the content is sym-linked to data modifiable at runtime (not recommended).
Properties
|
Property name |
Type |
Description |
|
host_name |
String |
Host name of the website. WEBx4 uses this name to display in automatically generated pages, as well as for constructing absolute URLs, for example, in server-generated redirects (for example, as may be set up in a custom config file installed on the content volume). Note: Although explicit redirects are rarely configured, a request for a directory without the trailing '/' causes a re-direct to be issued to the client, with the '/' appended; this redirect will use the value of host_name if it is set. |
|
admin_email |
String |
E-mail address for the server administrator. WEBx4 uses this name to display it in automatically generated pages. |
|
content_on_fs |
String |
Specifies whether the content is relative to the file system at the fs terminal or is on the content volume. Allowed values are on and off. If set to on, all content is relative to the file system at the fs terminal. If set to off, the content is on the content volume. |
|
docs_dir |
String |
Root directory on the content volume where the documents to be served are located. For example, it may be /mydocs. If docs_dir is set to the empty string, the root directory of the content volume is used. |
|
docs_loc |
String |
An optional location within the client-visible namespace where the content should appear ("client-visible namespace" is the path portion of a URL, or what appears to the right of the host name in a URL, including the leading /). If set to a non-empty value, this becomes the namespace root, as seen by the client, where the document root directory appears. For example, if docs_loc is set to subspace/samples, an HTTP request for /subspace/samples/file1.html will serve file1.html from the document root directory. Note that a request for a location outside /subspace/samples will return an error, except if it is a request for a script in the scripts directory (see scripts_loc). |
|
scripts_dir |
String |
Root directory on the content volume where CGI scripts are located. For example, it may be /scripts. This should be set to a non-empty value, referring to a directory on the content volume that contains only executable scripts (don't set it to "/"). |
|
scripts_loc |
String |
The location in the web space where the scripts directory specified by scripts_dir should be visible. This must be set to a non-empty string to enable the use of a dedicated scripts directory. A typical value may be /cgi-bin. Do not append a trailing slash to this value. |
|
logs_enabled |
String |
Controls whether WEBx4 will send its logs out the log terminal. Allowed values are on and off. If set to on, the log terminal must be connected. If this is set to off, no access log is used at all and the error log is written to a file on the root filesystem of the WEB servers, rotated weekly, with 4 weeks of back logs kept (/var/log/httpd/error_log*). Default: off |
|
logs_base_dir |
String |
Directory where WEBx4's logs are stored. This property has no effect if logs_enabled is set to off. Default: / |
|
error_log_level |
String |
Severity level of messages to be written to the error log. Allowed values are debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, alert and emerg. debug writes most messages, emerg writes only emergency messages. Default: warn |
|
srv2_standby |
Integer |
Specifies whether the second WEB5 server is in standby mode. If non-zero, the second WEB5 server is in standby mode, otherwise it is not in standby mode. |
|
srv3_standby |
Integer |
Specifies whether the third WEB5 server is in standby mode. If non-zero, the third WEB5 server is in standby mode, otherwise it is not in standby mode. |
|
srv4_standby |
Integer |
Specifies whether the fourth WEB5 server is in standby mode. If non-zero, the fourth WEB5 server is in standby mode, otherwise it is not in standby mode. |
|
timezone |
String |
Specifies the time zone used in the appliance. If this property is empty, the timezone is not modified and left as-is. A list of supported time zones is available here. Default: empty |
Important! All enumerated string properties are not case sensitive (lowercase). All other string properties are case sensitive.
Advanced Properties
These are additional properties that should typically not need to be configured. They can be used to tune up WEBx4 in non-standard circumstances. Properties which effect the operation of the load-balancer are prepended with lb, for example, lb_mode.
|
Property name |
Type |
Description |
|
lb_mode |
String |
Specifies the mode of operation and a way to use the named session cookie for session identification. Valid values are: |
|
lb_cookie_name |
String |
The name of the cookie used to identify a session. For the passive modes ( passive and sync - see the mode property below), this is the name of the cookie used by the back-end servers connected to out1 - out4 to identify client sessions. For the insert mode, this is the name of the cookie that HALB should insert into HTTP responses in order to make each client stick with a single server. If this property is set to the empty value, no session tracking is done and all requests are distributed in a simple round-robin fashion. Ignored for the source mode. |
|
lb_cookie_check_length |
Int |
Defines how many bytes from the value of cookie are used as unique key in passive mode of operation to match session to backend web server. Default value of 10 is usually sufficient for all common php and java applications. This value must always be equal or less than the length of the cookie value. |
|
lb_max_connections |
integer |
The maximum number of concurrently active connections that the load balancer handles. When this number is reached, new connections are still accepted, but their processing is delayed until another connection is closed. Upon start, load-balancer automatically determines the maximum number of connections based upon available memory, compares it to the value of this property and uses the lowest value. If this property equals 0 then the computed value is used. Note that neither the available memory nor an explicit setting of this property have a direct effect on the balancer's throughput or its maximum request rate - setting a low number (or having little memory) affects response only if the back-end servers are performing lengthy operations for each request (for example, database searches), causing many requests to remain open at the same time. |
|
lb_backup_outputs |
String |
A space or comma delimited list of outputs ( out1 - out4 ) that are considered backups. Traffic is directed to the backup servers only if all backend servers are unavailable. The purpose of these backup servers is to notify clients that something is wrong or redirect them, instead of throwing errors from unavailable backend or timing out. |
|
lb_healthcheck_url |
String |
The URL used to perform the health check of the backend web servers in http_get and http_head health check methods. May be specified as a complete URL (http://host.name/file/to/check/for.php) or as a relative path (/file/to/check/for.php). If specified as a URL, HALB uses the HTTP/1.1 protocol while performing the health checks using the hostname extracted from UR, in a Host: header. This allows usage of virtual hosts. If specified as a relative path, HALB uses the HTTP/1.0 protocol and checks for the document specified by this property. If this property is empty, load-balancer checks for the default root '/' using the HTTP/1.0 protocol. |
|
lb_healthcheck_agent |
String |
The string used as an agent identifier for http_get and http_head health check methods. If empty, "HALB-health-check" is used. |
|
lb_healthcheck_method |
String |
The method used for the health check of the backend web servers. |
|
lb_healthcheck_regexp |
String |
A test string used with the http_get health check mode. Short or common values (eg. OK) will likely cause false positive matches. This string is a perl regular expression, more details about perl regular expressions are available here. |
|
lb_healthcheck_interval |
Int |
Interval between health checks of the backend web servers (specified in seconds). |
|
lb_timeout |
integer |
Timeout in seconds to expire inactive sessions. If set to zero, inactive sessions do not expire. If set to a non-zero value, inactive sessions resumed after timeout seconds are considered stale, and requests bearing the 'forgotten' cookie are treated as if they have no cookie at all and are directed to a random server, using the usual round-robin method. This property is only valid for passive mode and ignored for all other modes. |
|
lb_client_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for waiting for a request from a client after establishing the connection. |
|
lb_server_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for waiting for a reply from a backend web server after establishing the connection. |
|
lb_conn_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for establishing any tcp connection. This includes the health checks. Extra attention must be paid to this setting, because if under high load the health checks time out because of insufficiently small value, load-balancer starts to disable outputs. It is not recommended to set it lower than 20 seconds. |
|
lb_username |
String |
Username for accessing the load-balancer GUI through the ui terminal. If empty, there is no authentication. |
|
lb_password |
String |
Password for accessing the load-balancer GUI through the ui terminal. Password is ignored if username is empty. |
|
lb_ctl_port |
Int |
Port that is used to access the web service control interface through the ctl terminal. |
|
lb_ui_port |
Int |
Port that is used to access the load-balancer runtime statistics GUI through the ui terminal. |
|
cgi_ext |
String |
Defines the file name suffixes for CGI scripts as a space-separated list. This is used to specify which files to treat as executable CGI scripts (in any directory) and can be used as an alternative to specifying a common scripts directory - see the scripts_dir and scripts_loc properties. Default: .cgi |
|
shared_perl_ext |
String |
Defines the file name suffixes for in-process Perl scripts as a space-separated list. This is used to specify which files to treat as Perl scripts to be run with mod_perl. Any extension that matches one already specified in cgi_ext overrides the use of CGI for that extension and configures it to be run by mod_perl instead. The in-process Perl module is configured to run scripts with the specified extensions in CGI compatibility mode - most Perl scripts designed to be run as CGI processes should work if set up as in-process scripts as well. Note: it is important to check your scripts for proper initialization of all file-scope variables, for example, with use strict; use warnings; , since all scripts run by mod_perl execute without re-starting the Perl interpreter. If unsure whether your scripts will work with mod_perl, review the mod_perl documentation for more information: http://perl.apache.org/docs/index.html. |
|
index_files |
String |
Ordered, space-separated list of files to use as a directory index page in case the client requests a URL that refers to a directory name. |
|
use_htaccess |
String |
Specifies whether to enable the use of .htaccess files for the entire document tree. This is disabled by default and should be used only if you have a content directory structure that requires fine-grain control of server options, but is too complicated to configure using a set of sections in a common config file, or if you have a pre-configured content volume that already uses .htaccess and want to avoid the hassle of re-arranging it. If config options are needed only for the document root itself, put your settings in the document root directory in the .htconf file instead - they will be applied exactly the same way as for .htacces, except the file is read once at boot time. Default: off |
|
max_connections |
Integer |
Maximum number of concurrent active connections that each WEB5 server can handle. If this limit is reached, additional connection requests are queued (up to a limit of 511) and processed as currently active connections get closed. This value should be raised only if WEBx4 is expected to serve a large number of requests that need access to a slow external source of data (for example, lengthy database queries). The actual number of concurrent connections may be limited below the value set for this property, if there is not enough system memory. See the Memory Usage section. The max_connections value cannot be set to more than 256. |
|
persistent_connections |
String |
Controls whether WEBx4 allows clients to request more than one document on the same connection. Allowed values are on, off. You may need to disable the persistent connections only if you have problems with clients that do not support HTTP/1.1 properly but don't fall back to HTTP/1.0. Default: on |
|
idle_timeout_sec |
Integer |
Timeout, in seconds, for keeping a client connection open if there is no request or response going through. This property is used only if persistent_connections is on. Keeping this timeout short helps drop forgotten connections quickly. Default: 15 |
|
data_timeout_sec |
Integer |
Timeout, in seconds, for receiving or sending more data if a data transfer has started but is not completed. Having this timeout allows WEBx4 to drop connections that got forgotten, while still allowing delays during the transfer. Default: 300 |
|
default_charset |
String |
Default character set to report for returned documents of type text/html or text/plain. The property should be set either to the name of a character set or to off (to disable sending of a charset header in HTTP responses). For some browsers setting this property can override the character set value provided by the author of the served HTML documents and is therefore recommended only if there are documents that do not contain a valid character set specification and it is known in advance that all documents served by WEBx4 are in the same character set. Typical example values may be iso-8859-1 or utf-8. Default: Off |
|
info_level |
String |
Controls how much information WEBx4 discloses about itself to web clients (in HTTP responses and in automatically generated pages). Allowed values are full (most info), os, minor, major, prod (least info). As a security measure, it is recommended that you disclose the minimum information. Default prod |
|
server_signature |
String |
Controls whether WEBx4 appends a server signature line at the bottom of all generated pages (for example, on error pages). Allowed values are on, off. The amount of information WEBx4 includes in the signature is controlled by info_level. Default off (no signatures). |
|
env |
String |
Used to pass settings to WEBx4 as name=value pairs. Default: (empty) |
Important! All enumerated string properties are not case sensitive (lowercase). All other string properties are case sensitive.
Each WEB5 server in WEBx4 configures itself automatically to run with a wide range of available memory, to fit applications of different size and load. Despite this, please note that the configuration calculation cannot predict the memory usage of dynamic-content scripts that may be installed on the content volume and a misbehaving script can cause the server to malfunction by overcommitting memory and causing the OS to kill processes.
By default, each WEB5 configures the maximum number of active connections assuming:
For example, in the sandbox configuration with 32M, the max number of active connections will be set to 8.
The maximum number of connections can be limited below the automatically computed value using the max_connections property. Remember that if max_connections is above the limit imposed by the available system memory, it is trimmed without warning.
In addition, the PHP pre-processor's allocation limit is set to 1/2 the memory available for scripts, as computed according to the above rules, that is, the PHP is configured to limit the memory for a running script to
(system_memory - 16MB - max_connections * 1MB) / 2
Where the max_connections value is the smaller of the max_connections property and the limit imposed by the available memory (computed assuming 2MB per connection, as described above). If the max_connections property is left at its default value, this will yield the following value for the PHP memory limit:
(system_memory - 16MB) / 4
Note: The "1/2 of available memory per script" rule used is somewhat optimistic and is based on the assumption that either not all active connections will use a hungry PHP script that actually hits the limit, or that the scripts do not actually use all the memory that they allocate.
TIP: If a memory-heavy application starts misbehaving under load (drops connections), and increasing the available memory is not an option, try setting the max_connections property to a lower value. This will reduce the possible number of script instances that run at the same time, giving each instance more memory to run in.
This section provides useful information for configuring scripts that serve dynamic content.
On starting the HTTP server, the following directories and files are available within the filesystem space of each WEB5 instance. Note that using absolute directory names outside of these locations in any script or configuration file is not recommended.
/var/www/html - web root, visible as '/' to the client. This refers to a location on the content volume and is read-only. Note that if the 'docs_loc' property is set, then /var/www/html itself will have no data files in it. Appending the value of docs_loc will produce the name of a valid symbolic link that refers to the document root. This directory name and the /var/www/cgi-bin name and any of their sub-directories can be used in Apache configuration files to set up additional per-directory settings. This avoids the need for such configuration files to be aware of the particular setting for the docs_dir and scripts_dir properties.
/var/www/cgi-bin - symbolic link to the scripts root, if set up using the scripts_dir property.
/mnt/fs - root of the shared read/write file storage provided by a CIFS server connected to the 'fs' terminal. If one is not connected, /mnt/fs will be empty.
The /icons/ path is aliased to a directory containing stock icons for server-generated directory listings. Therefore, a directory named icons in the content volume will not be visible.
The HTTP server runs as user 48, group 48. CGI scripts run in the same context.
Files on the content volume should have 'read' permission for everyone, to be eligible for serving through HTTP. Executable scripts should have 'read' and 'execute' permissions for everyone.
Although the Apache server has other means to control access to files, one may also remove the read permission for everyone from files or directories that should not be made accessible through HTTP. Do leave the x bit set on for directories for which a listing should not be accessible, but contain files or sub-directories that are accessible.
The sendmail system is not configured on WEBx4. Do not use it for sending e-mail from this appliance. If using Perl-based scripts, the Mail::Mailer module can be used for sending e-mail, if it is configured to use the smtp mailer. In all cases, your SMTP mailer should be set up to use aux as the hostname of the SMTP server, for example, if using Mail::Mailer :
$mailer = new Mail::Mailer 'smtp', (Server => 'aux');
$mailer->open(\%headers); #... etc.
The following is the interior of WEBx4.
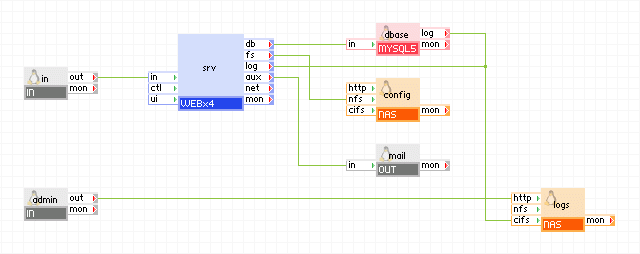
For problems and suggestions, contact Technical Support.
|
Copyright © 2011 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|