

Using Your Development Environment › Setting Up the User Environment › Automatic Naming Algorithm
Automatic Naming Algorithm
If you use automatic naming,CA 2E assigns a name according to an algorithm when you create a new entity, such as a field, file, or function, and ensures that the name is unique across the model. The following diagram summarizes how names are assembled for Objects/Members (programs/files), Formats, and Fields.
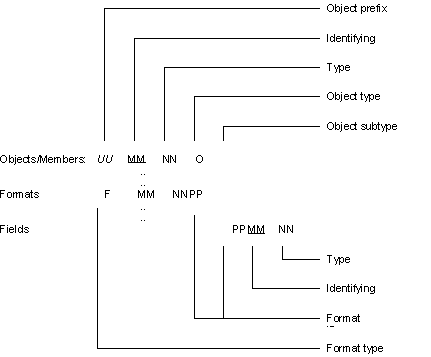
The following explains the elements in the illustration:
- UU—The object prefix is derived from the model value YOBJPFX which contains the value stored in the file YALCVNMRFP.
-
- MM—The identifying mnemonics are a unique, arbitrary pair of letters read from the file YALCVNMRFP. Each object type has a different set of identifying mnemonics that correspond to different records in the file YALCVNMRFP.
-
- For example, physical and logical files will use the next available value in Object type FIL. Functions, including the CLP for query access paths, will use the value in Object type MSG.
-
- Model value YFILPFX contains the last identifying mnemonic used for defining files; see the note following this list for more information.
-
- NN—The type mnemonics are a pair of letters allocated according to the CA 2E object attribute. For example, fields of type CDE are CD and query access path CLP programs are QF.
-
- O—The object type is a single letter that identifies object types; for example, P (physical file), L (logical file), R (RPG program), or C (CLP program). You can set up the values to be used by the object types by using the Edit Generation Types panel. For functions, the object sub-type distinguishes between the help and display file associated with the PGM object type.
-
- X—The object sub-type is a single letter that depends on the object type. For logical files, this letter indicates the access path number. For display files and help member or panel groups, you can set up the values to be used by the object sub-types by using the Edit Generation Types panel.
-
- F—The format type is a single letter that identifies the format type; for example, @ for database files or # for display files. You can set the values to be used by the object types using the Edit Generation Types panel.
-
- PP—The format ID (PP) is an arbitrary set of letters unique for each physical file.
-
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


