

The following examples focus on the CA 2E relation types: Owned by, Known by, Qualified by, Has, and Refers to.
Example 1: Simple Sales Ledger
You have a number of customers who order your products. Each order can involve a number of different products but can be issued to only one customer. Customer and Product are identified by Customer code and Product code respectively; an order is identified by an Order number that is unique within the business. Each Order is made up of an Order header and a variable number of Order detail lines, each of which is for a particular quantity of a particular Product.
The situation can be represented diagrammatically as follows:
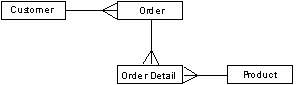
We could model this situation by using the CA 2E relation statements described below.
FIL Customer REF Known by FLD Customer code CDE
FIL Customer REF Has FLD Customer name TXT
The key of the Customer file is the Customer code.
FIL Product REF Known by FLD Product code CDE
FIL Product REF Has FLD Product name TXT
FIL Product REF Has FLD Product size NBR
FIL Order CPT Known by 1 FLD Order code CDE
FIL Order CPT Has 2 FLD Order date DT#
FIL Order CPT Has 3 FLD Order status STS
FIL Order CPT Refers to 4 FIL Customer REF
FIL Order Detail CPT Owned by 1 FIL Order CPT
FIL Order Detail CPT Known by 2 FLD Order line no NBR
FIL Order Detail CPT Has 3 FLD Order quantity QTY
FIL Order Detail CPT Refers to 4 FIL Product REF
The previous relations result in the following entries in the files:
|
|
Product |
|
|
Customer |
|
K |
Product code Product name Product size |
|
K |
Customer code Customer name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Order |
|
|
Order Detail |
|
K |
Order code Order date Order status Customer code |
|
K K |
Order code Order line no Order quantity Product code |
Example 2: A More Complicated Product Structure
Your products have a more complicated structure than first imagined. Each Product belongs to a Product group that serves as part of the product identifier. Each Product also has a Product type that is not part of the product identifier, but has some extra information associated with it. We can refine the model to reflect this situation by adding a Product group and a Product type file.
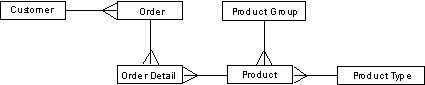
A Product group could be described as follows:
FIL Product group REF Known by FLD Product group code CDE
FIL Product group REF Has FLD Product group name TXT
A Product type could be described as follows:
FIL Product type REF Known by FLD Product type code CDE
FIL Product type REF Has FLD Product type name TXT
FIL Product type REF Has FLD Pack size QTY
FIL Product type REF Has FLD Freight charge VAL
The definition of a Product could then be amended by adding an Owned by relation to associate each Product with Product Group and a Refers to relation to associate a Product type with each Product.
FIL Product REF Owned by Product group FIL REF
FIL Product REF Known by Product code FLD CDE
FIL Product REF Has Product name FLD REF
FIL Product REF Has Product size FLD QTY
FIL Product REF Refers to Product type FIL REF
We now have entries on two new files, the Product group and the Product type. A new entry for the Product group code has been added wherever the Product file was referenced by other CA 2E files, in this case, on the Order details:
|
|
Product Group |
|
|
Product Type |
|
K |
Product group code Product group name
|
|
K |
Product type code Product type name Pack size Freight charge |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product |
|
|
Order Detail |
|
K K |
Product group code Product code Product name Product size Product type code |
|
K K |
Order code Order line no Order quantity Product group code Product code |
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|