Programming and Coding Examples › General Rules for Preparing Command Diagrams › Example
Example
- If additional information about a parameter is required, enter a number enclosed in brackets against the parameter, and explain it at the bottom of the diagram.
- Use ‘>’ before a parameter value to indicate that it is the default value.
- Use ‘-|’ and ‘|-’ to indicate a fork in a syntax base or branch line.
- Use ‘——’ to indicate the termination of the syntax base line (for example, no ‘*’ or ‘’), and continue the line to the edge of the diagram:
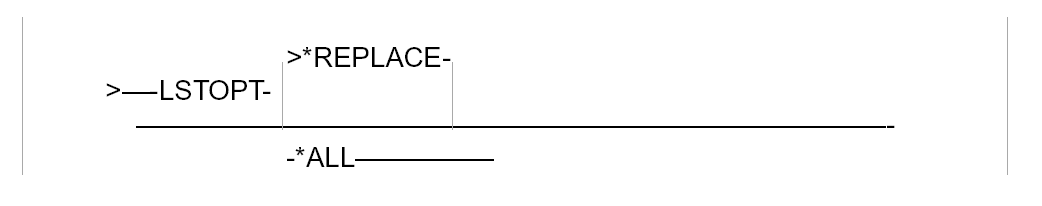
- For qualified object names, place ‘/’ after an element name to indicate qualification.
- Place a box containing a ‘P’, after the last permitted positional parameter:

- Place a box containing a ‘K’, after the last permitted keyword parameter.
- Draw a line across the diagram to indicate the last required parameter. Place the word ‘Required’ above this line on the right-hand side. Place ‘Optional’ below this line. If all parameters are optional, place ‘Optional’ in the top left hand corner of the box.

- To indicate variables, use lower case and connect compound nouns with hyphens, for example, ‘library-list-name’. Values should be of a data type, rather than a specific name, for example ‘date’ rather than ‘order- date’.
- For parameters that have a choice of values, place each value on a different branch line. If more than one value can be specified, indicate this with an arrow below, and state the maximum number of allowed values. For example:
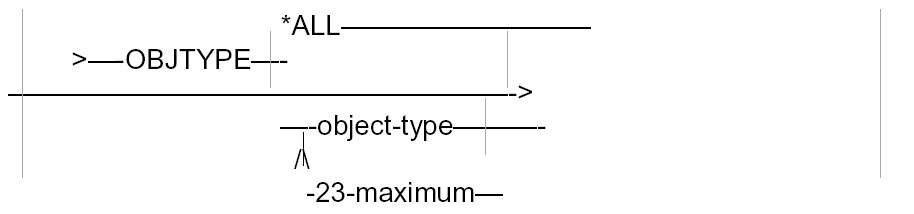
- State the environments in which the command may be used (interactive or batch) in a box at the bottom right-hand corner of the command diagram. List the modules of the product for which the command is applicable, underneath the command diagram. For example:





