Business-to-Business (B2B) encryption lets you share encrypted tapes between one organization and another using digital certificates. This requires the sharing of the digital certificates between the two sites. For example, Company A wants to receive its data from Company B in encrypted form. To do this, Company A must do the following:
Company B must import the digital certificate into the security system database at that site.
The following diagram shows how a business partner, Company A, prepares a digital certificate and sends it to Company B, the site that will create the encrypted tape:
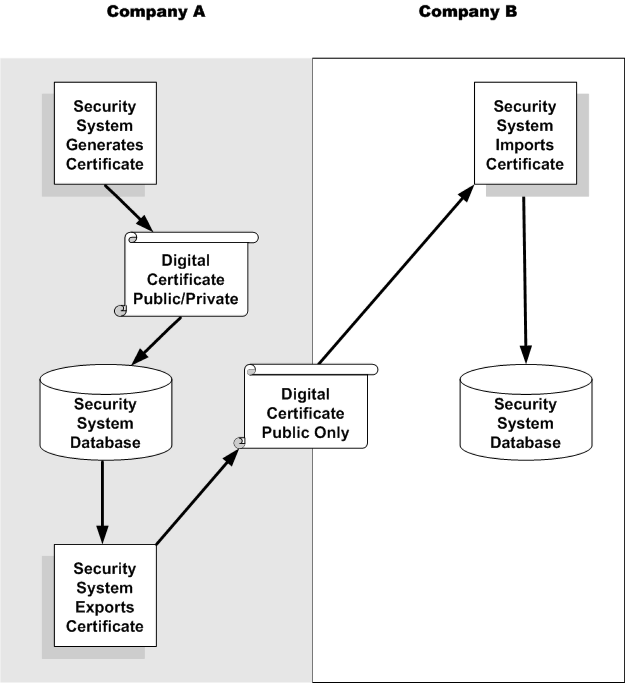
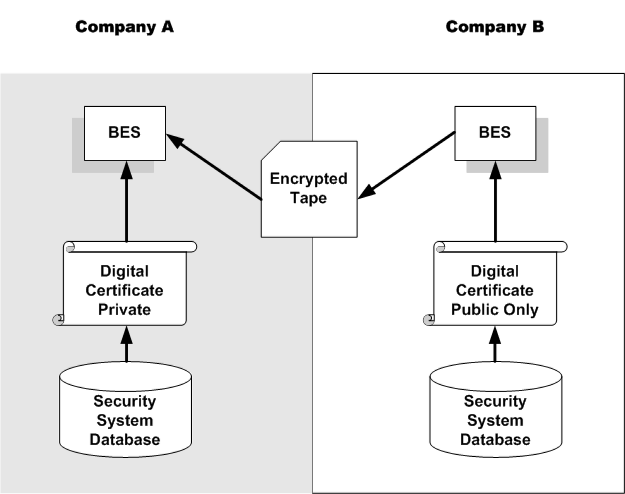
The BES system at Company B's site generates a symmetric key to encrypt the data. It uses Company A's public key to encrypt the symmetric key, which it stores in the tape's header labels, along with the name of the digital certificate. It then encrypts the data using the symmetric key. The tape contains both the encrypted data and the symmetric key that must be used to decrypt it. Because the symmetric key is encrypted, both the key and the data are secure. When Company A receives the tape, the BES system in Company A recognizes the name of the digital certificate in the tape headers and retrieves the private key from the security system. The private key is used to decrypt the symmetric key in the tape header labels. That symmetric key is then used to decrypt the tape data.
The following diagram shows how Company B uses the public key from Company A's digital certificate to encrypt a tape, and how Company A uses its own private key to decrypt the tape received from Company B:
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Tell Technical Publications how we can improve this information |