The Scheme Setup tab for SAML 1.x artifact authentication is where you specify how the consumer communicates with the producer to retrieve the assertion, authenticate a user based on that assertion, then direct the user to the target resource.
The fields on the Scheme Setup tab of the SAML Artifact Template are as follows:
Names of the consumer. Enter an alphabetic string, for example, CompanyA.
The name you enter here must match a name of a consumer in the Affiliate domain at the producer site.
Important! For the SAML artifact profile, the producer sends the assertion over a protected back channel to the consumer. If you are using basic authentication to protect the back channel, the value of this field is the name of the consumer. If you are using client certificate authentication for the back channel, the value of this field is the alias of the client certificate stored in the smkeydatabase.
Indicates the method by which the SAML credential collector redirects the user to the target resource. If you select 302 No Data or 302 Cookie Data, no other configuration is required. If you select Server Redirect or PersistAttributes, there is additional configuration required.
Redirects user through an HTTP 302 redirect with a session cookie, but no other data.
Redirects user through an HTTP 302 redirect with a session cookie and additional cookie data configured at the site that produced the assertion.
Enables header and cookie attribute information, which is received as part of a SAML assertion, to be passed to the custom target application. The SAML Credential Collector transfers the user to the target application URL by using server-side redirect technology. Server-side redirects are part of the Java Servlet specification, and are supported by all the standard-compliant servlet containers.
To use this mode, you must follow these requirements:
All target application files need to be in the application’s root directory. This directory is either:
—Web Agent: web_agent_home\webagent\affwebservices
—SPS federation gateway: sps_home\secure-proxy\Tomcat\webapps\affwebservices
Java servlet technology allows applications to pass information between two resource requests using the setAttribute method of the ServletRequest interface.
The service that consumes assertions sends the user attribute to the target application by setting different attribute objects in the request object before redirecting the user to the target application.
The service creates two java.util.HashMap objects--one to store all header attributes and one to store all cookie attributes. It uses distinguished attribute names to represent each hashmap object:
—Netegrity.HeaderAttributeInfo attribute represents the hashmap that contains header attributes.
—Netegrity.CookieAttributeInfo attribute represents the hashmap that contains cookie attributes.
Two other Java.lang.String attributes are set by the assertion consuming service to pass the user identity to the custom application:
—Netegrity.smSessionID attribute represents the SiteMinder session ID
—Netegrity.userDN attribute represents the SiteMinder user DN.
The custom target application at the customer site can read these objects from the HTTP request object and can make use of the data found in the hashmap objects.
Redirects the user through an HTTP 302 redirect with a session cookie, but no other data. Additionally, this mode instructs the Policy Server to store attributes extracted from an assertion in the session store so they can be supplied as HTTP header variables. For additional configuration, see the instructions for using SAML attributes as HTTP headers.
Note: If you choose PersistAttributes and the assertion contains attributes that are left blank, a value of NULL is written to the session store. This value acts as a placeholder for the empty attribute and it is passed to any application using the attribute.
Defines the password that the consumer uses to identify itself to the producer.
This password must match the password entered for the consumer at the producer site.
Confirms the password that you specified in the Password field.
Defines the source ID of the producer.
The SAML specification standard defines a source ID as a 20-byte binary, hex-encoded number that identifies the producer. The consumer uses this ID to identify an assertion issuer.
Enter a number that matches the Source ID that the producer uses. At the producer, this ID is located in the SAML assertion generator properties file, AMAssertionGenerator.properties, which is located in the following directory:
policy_server_home/config/properties
The default Company Source ID value is: b818452610a0ea431bff69dd346aeeff83128b6a
Specifies the version of the SAML specification with which the assertion is generated. The choices are 1.0 or 1.1. SAML 1.1 is the default.
There must be a match between the SAML protocol and assertion versions used by the producer or consumer. For example, if a producer using SAML 1.1 receives a SAML 1.0 request, it returns an error. If a consumer using SAML 1.1 receives a SAML 1.0 assertion embedded into a SAML 1.1 protocol element, it returns an error.
Defines the URL of the service at the producer where the consumer retrieves the SAML assertion. Specifically, this URL identifies the location of the Assertion Retrieval Service, which must be a URL accessed over an SSL connection.
If the assertion retrieval service at the producer is part of a realm using the Basic over SSL authentication scheme, the default URL is:
https://idp_server:port/affwebservices/assertionretriever
Identifies the web server and port hosting the Web Agent Option Pack or SPS federation gateway.
If the assertion retrieval service at the producer is part of a realm using the X.509 client certificate authentication scheme, the default URL is:
https://idp_server:port/affwebservices/certassertionretriever
Identifies the web server and port hosting the Web Agent Option Pack or SPS federation gateway.
Specifies the authentication method for the realm at the producer that contains the Assertion Retrieval Service. The value of this field determines the type of credentials that the SAML credential collector at the consumer must provide to access the Assertion Retrieval Service and retrieve the SAML assertion.
The Assertion Retrieval Service retrieves the assertion from the Policy Server at the producer, and then sends it to the consumer across an SSL back channel. We recommend protecting the Assertion Retrieval Service.
Select one of the following:
When you select this option, configure access to the Assertion Retrieval Service with a client certificate.
Depending on the authentication method you select, there can be some additional configuration required.
For client certificate authentication, you can use non-FIPS 140 encrypted certificates to secure the back channel even if the Policy Server is operating in FIPS-only mode. However, for FIPS-only installations use certificates only encrypted with FIPS 140-compatible algorithms.
Defines the audience for the SAML assertion.
The Audience identifies the location of a document that describes the terms and conditions of the business agreement between the producer and the consumer. The administrator determines the audience at the producer site. It also must match the audience specified for the consumer at the producer.
The audience value must not exceed 1 K.
To specify the audience, enter a URL. This element is case sensitive. For example:
http://www.companya.com/SampleAudience
Identifies the producer that issues assertions for the consumer. This element is case sensitive.
For example, producerA.ca.com
The consumer accepts assertions from only this issuer. The administrator at the producer determines the issuer.
Note: The value that you enter for the issuer must match the value of the AssertionIssuerID at the producer site. This value is specified in the AMAssertionGenerator.properties file located in: siteminder_home/Config/properties/AMAssertionGenerator.properties
Defines an Xpath query that tells the authentication scheme where to look in the SAML assertion for data used to look up a user in the user directory. The Xpath query and the Search Specification value map data from a SAML assertion to a user store entry.
Xpath queries should not contain namespace prefixes. The following is an invalid Xpath query:
/saml:Response/saml:Assertion/saml:AuthenticationStatement/ saml:Subject/saml:NameIdentifier/text()
The valid Xpath query is:
//Response/Assertion/AuthenticationStatement/Subject/ NameIdentifier/text()
Select the namespace and click Edit to the right of the search specification scroll box. The SiteMinder Authentication Scheme Namespace Mapping dialog box opens. In this dialog, you map the data collected by the Xpath query to a namespace attribute.
Example:
The following query extracts the text of the Username attribute from the assertion:
"/Assertion/AttributeStatement/Attribute/AttributeValue/SMContent/SMlogin/Username/text()"
"//Username/text()" extracts the text of first Username element in the SAML assertion using abbreviated syntax.
Other examples:
"substring-after(/Assertion/AttributeStatement/Attribute/AttributeValue/ SMContent/SMprofile/NVpair[1]/text(),"header:uid=")"
This query string extracts the text of the header attribute named "uid" configured as the first attribute in the Affiliate dialog at the producer site.
Using the following abbreviated syntax extracts the text of the header attribute named "uid" configured as the first attribute in the Affiliate dialog at the producer site using abbreviated syntax:
"substring-after(//SMprofile/NVpair[1]/text(),"header:uid=")"
Specifies the alias of the public key in the smkeydatabase that is used to verify the digital signature which signed the assertion. This alias is associated with the certificate in the smkeydatabase. When you list the certificates in the smkeydatabase, the type of certificate used for verification is a CertificateEntry or KeyEntry certificate.
Selectable list of namespace types and defined search specifications.
Enter the attribute that the authentication scheme uses to search a namespace.
Opens the Authentication Scheme Namespace Mapping dialog where you can enter a Search Specification which defines the attribute that the authentication scheme uses to search a namespace. Use %s in the entry as a variable representing the assertion data collected by the Search Data XPATH query.
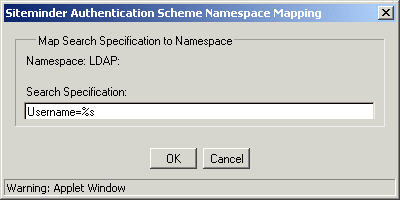
For example, the XPATH query retrieves the value of user1 for the Username attribute in the SAML assertion. If you specify Username=%s in the Search Specification field, the resulting string is Username=user1. Compare this string against the user directory to find the correct record for authentication.
Selecting this button displays the SAML 1.x Auth Scheme Properties dialog for the authentication scheme. From this dialog, you define the message consumer plug-in, redirect URLs for failed authentication, and the target federation resource.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |