Federation Security Services Guide › Authenticate WS-Federation Users at a Resource Partner › Supply SAML Attributes as HTTP Headers › Use Case for SAML Attributes As HTTP Headers
Use Case for SAML Attributes As HTTP Headers
During authentication, a series of SAML attributes are extracted from an assertion and supplied as HTTP headers. During the authorization process, these headers are returned to the customer's application.
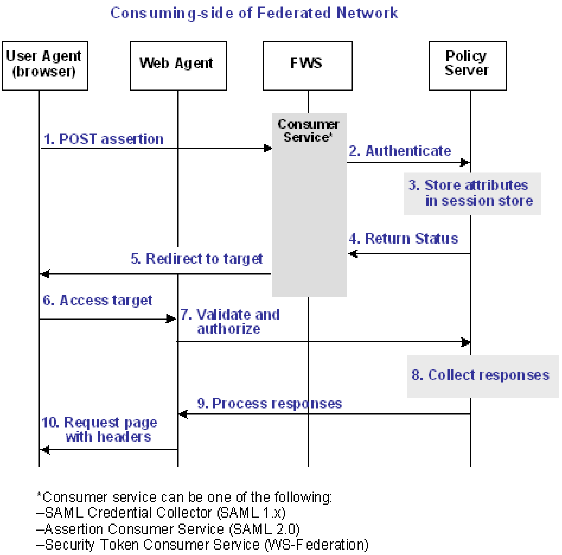
The following flow diagram shows the sequence of events at runtime:
Note: The SPS federation gateway can replace the Web Agent and Web Agent Option Pack to provide the SiteMinder Federation Web Services application functions. In the flow diagram, the Web Agent block would be the embedded Web Agent in the SPS federation gateway. For information about installing and configuring the SPS federation gateway, see the CA SiteMinder Secure Proxy Server Administration Guide.
To process the attributes as HTTP headers, the sequence of events is as follows:
- After the assertion is generated at the producing partner, it sends the assertion to the appropriate consumer service at the consuming partner. The delivery mechanism (POST or Artifact or WS-Fed) is irrelevant.
Note: The consumer service can be the SAML credential collector (SAML 1.x), the Assertion Consumer Service (SAML 2.0), or Security Token Consumer Service (WS-Federation).
- The consumer service calls its local Policy Server to use the configured authentication scheme to authenticate the user with the assertion.
- If the authentication scheme's redirect mode parameter is set to PersistAttributes, the Policy Server caches the attributes in the session store as session variables.
- The result of the authentication is returned to the consumer service.
- The consumer service redirects the browser to the protected target resource.
- The browser tries to access the target resource.
- The Web Agent calls the Policy Server to validate the user's session and to ensure the user is authorized to access the target resource.
- The Policy Server retrieves the attributes by a configured response.
- The Policy Server processes the responses and sends the attributes to the Web Agent.
- The Web Agent sets the HTTP headers as necessary.
