A policy domain is a logical grouping of resources associated with one or more user directories. In addition, policy domains require one or more administrator accounts that can make changes to the objects within the policy domain. Policy domains contain realms, rules, responses, and policies (and optionally, rule groups and response groups). An administrator with the appropriate privileges assigns a policy domain to one or more administrators. For information about administrator privileges, see Policy Server Administrators.
The resources in a policy domain can be grouped in one or more realms. A realm is a set of resources with a common security (authentication) requirement. Access to resources is controlled by rules, which are associated with the realm that contains the resource. The following diagram illustrates a small policy domain which contains realms and their associated rules, as well as a rule group, response group, and a pair of responses.
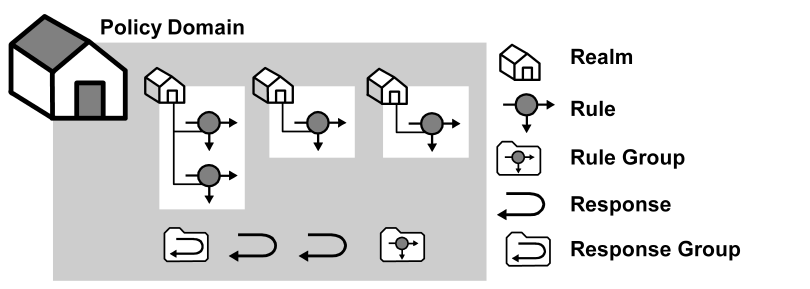
By grouping realms and rules in a policy domain, you can provide organizations with a secure domain for their resources. In the policies section, you learn how to create policies within a policy domain to control access to the policy domain's resources.
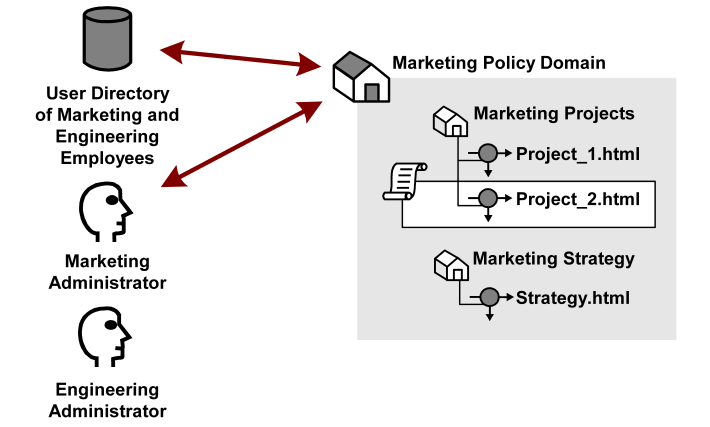
In the sample diagram below, a Marketing policy administrator who is specified in the Marketing policy domain can manage the Marketing Strategy and Marketing Projects realms. The policy domain ensures that the Engineering administrator, who does not have administrative privileges to manage the Marketing policy domain, cannot control resources belonging to the Marketing department. However, the Marketing policy domain is associated with a user directory that contains engineering users.
If the administrator for the Marketing department creates a policy within the Marketing policy domain that allows Engineering staff to access the resource Project 2.html, engineering users may access the resource.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |