An LDAP directory's topology describes the division of a directory tree among physical servers. The logical sections of a directory tree are called partitions. LDAP directory topology varies widely between LDAP deployments, but regardless of the topology, the use of referrals between partitions allows the directory to function as a single service.
Three types of LDAP referrals can be employed in a directory topology. These types can be used in conjunction to create very complex directory structures. The types are:
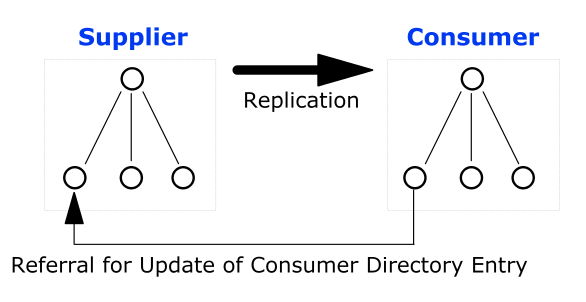
When a directory topology includes a replication agreement, all changes in a supplier directory are replicated (duplicated) in a second consumer directory. The consumer and supplier directories may be used to load balance requests, or may have a failover relationship. When an update request is received by the consumer directory, the consumer directory refers the request to the supplier directory where the update is completes. This is a very common type of LDAP referral.
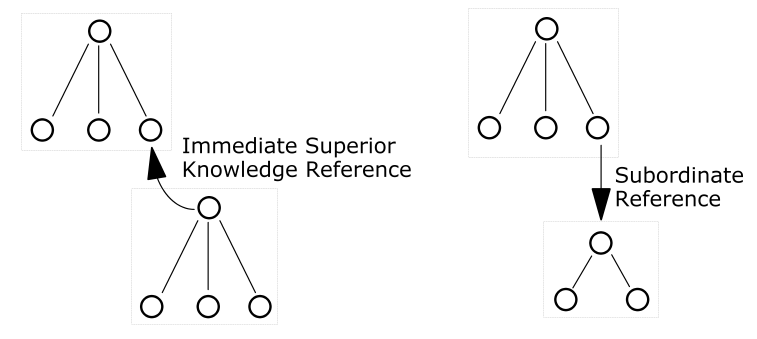
Pointers from one directory partition to another are called knowledge references. Knowledge references that point to the node immediately upward toward the root in the DIT are considered immediate superior knowledge references. Knowledge references that point downward in the DIT to other partitions are considered subordinate references.
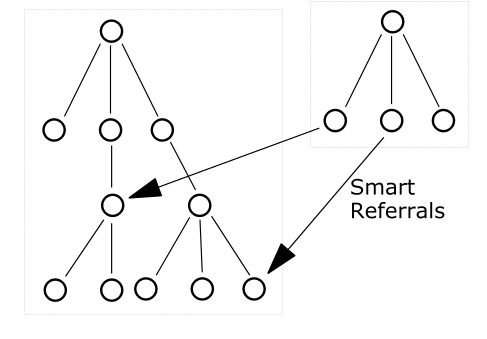
A pointer to a location in a portion of the directory that is not immediately above or below the original partition s called a smart referral. A smart referral contains enough information to see a node anywhere in the directory topology.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |