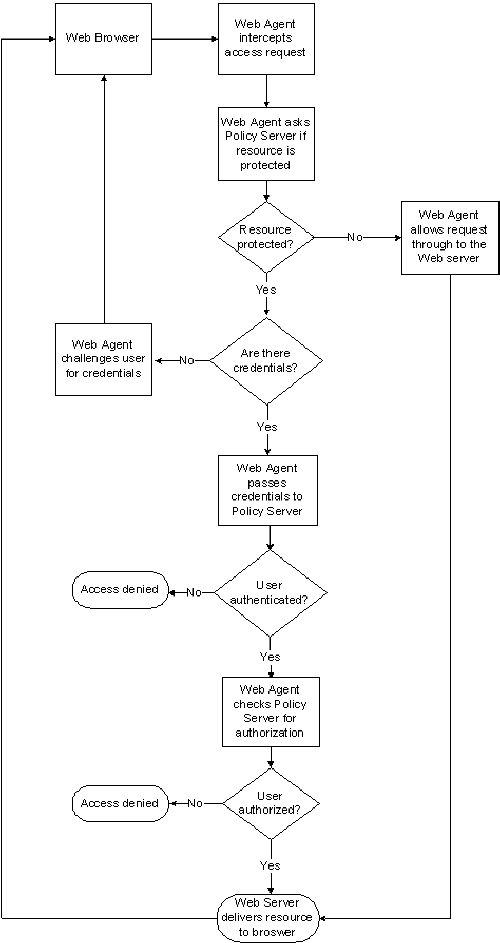
To enforce access control, the Web Agent interacts with the Policy Server, where all authentication and authorization decisions are made.
The Web Agent intercepts user requests for resources and checks with the Policy Server to see if the requested resource is protected. If the resource is unprotected, the access request proceeds directly to the web server. If the resource is protected, the following occurs:
The user responds with the appropriate credentials.
The Web Agent also receives user-specific attributes, in the form of a response, to enable Web content personalization and session management. A response is a personalized message or other user-specific information returned to the Web Agent from the Policy Server after authorizing the user. It consists of name-value attribute pairs that are added to HTTP headers by the Web Agent for use with Web applications. Examples of responses include the following:
The following diagram shows the communication between the Web Agent and the Policy Server:
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |