Implementation Guide › Architectural Considerations › Architectural Use Cases › Redundancy and High Availability › Agent to Policy Server Communication › Policy Server Clusters
Policy Server Clusters
Round robin load balancing evenly distributes Web Agent requests to all Policy Servers that the HCO lists. Although an efficient method to improve system availability and response times, consider that:
- Round robin load balancing is not the most efficient distribution method in a heterogeneous environment where computing capacity can differ. Each Policy Server receives the same number of requests, regardless of capacity.
- Round robin load balancing to Policy Servers that are located in different geographical locations can degrade performance. Sending Web Agent requests to Policy Servers outside a certain locale can result in increased network communication overhead and network congestion.
A Policy Server cluster is a group of Policy Servers to which Web Agents can distribute requests. Policy Server clusters provide the following benefits over round robin load balancing:
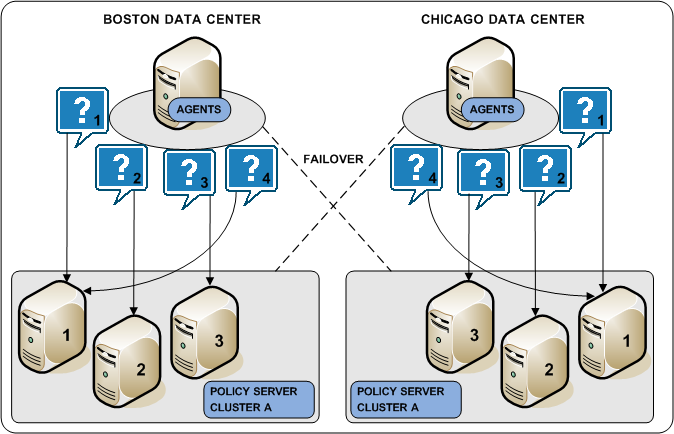
- A cluster can be configured to include Policy Servers only in a specific data center. Grouping Web Agents with distinct Policy Server clusters avoids the network overhead involved with load balancing across geographically separate regions. Network overhead is only incurred if Web Agents failover to another Policy Server cluster.
- A cluster can failover to another cluster based on a Policy Server failover threshold.
- Web Agents dynamically distribute requests across all Policy Servers based on response time, instead of distributing requests evenly.
Note: For more information about configuring a Policy Server cluster, see the Policy Server Administration Guide.
The following diagram illustrates two Policy Server clusters. Each cluster is geographical separated to avoid the network overhead that can be associated with round robin load balancing.