Implementing Processes › How to Implement Processes
How to Implement Processes
A process is a series of steps that can be executed in sequence to perform complex processing.
You define processes to automate complex operations tasks.
Processes can be executed as follows:
- From a resource definition—you can specify a process in a resource definition. The process is invoked when required for that resource.
- From an availability map—you can specify a process in an availability map (for example, to perform tasks at particular times).
- From an event rule—you can specify a process in an event rule. The process is invoked when an event triggers the rule.
- As a single task—you can run a process as a single, independent task. Use this feature to debug processes or as a quick way of executing a process manually.
- Interactively—you can run a process in the INTERACTIVE mode. Use this feature to check the results of processing single steps, or of processing a sequence of steps one at a time. You can display individual step logs and, if required, change the step parameters.
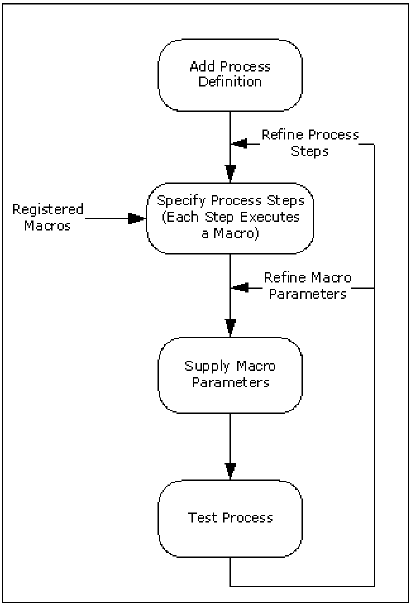
The following illustration shows the typical stages in defining a process.
Process Types
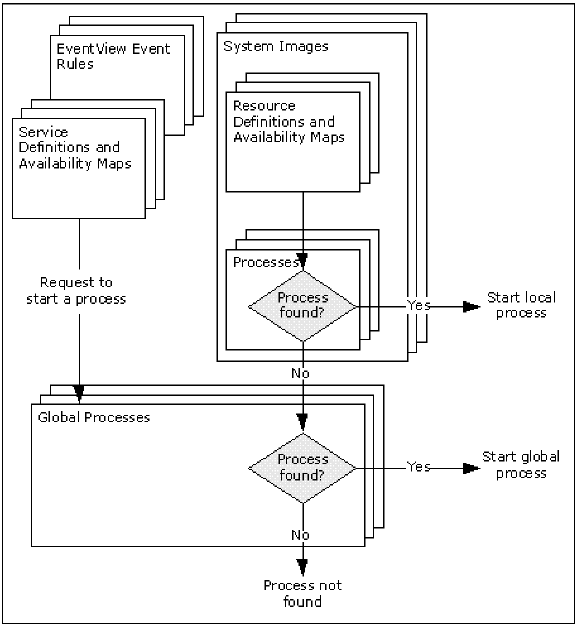
A process can be global (available to all components) or local (available to a specific system image only). A global process is available to all components; however, a local process is available only if it belongs to the local active image.
ServiceView and EventView components can use global processes only. ResourceView components can use both types of processes, according to the following rules:
- If a process is required and one exists in the local active system image, that process is used.
- If the required process does not exist in the active system image, the global process of the same name is used.
The following illustration shows how processes are searched for execution.