The record key used when processing a base cluster UDB can be 1 to 255 bytes in length and usually starts at offset 0 in the record.
When accessing a base cluster by an alternate index, a key is still used, but the key could be located anywhere within the record that it identifies. The precise location of the key within the record is defined (as an offset from the start of the record) when the alternate index is defined.
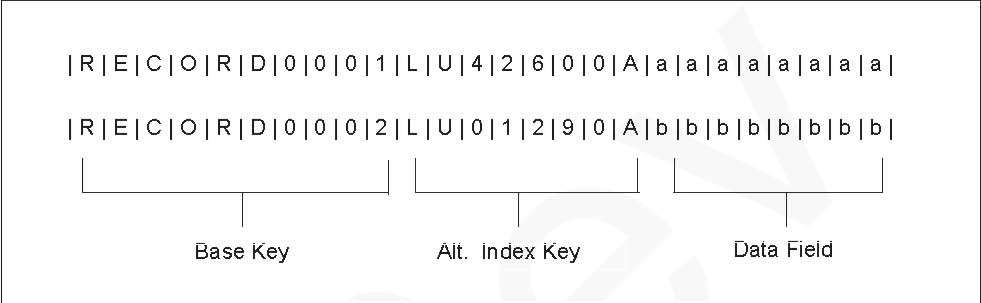
This figure shows a representation of two records on a base cluster. The base key of each record starts at offset 0 and is 10 bytes long. In the example the base keys of the two records are:
RECORD0001 RECORD0002
An alternate index is associated with the base cluster and has been defined with a key that is 8 bytes long and starts at offset 10 in the record, that is, it follows the base key of the record.
In the example the alternate index keys have values of:
LU42600A LU01290A
Additional alternate index keys can be defined which span different strings within the base cluster record.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Tell Technical Publications how we can improve this information |