Installation Guides › Implementation Guide › SOA Security Manager Introduction › SOA Security Manager Overview › SOA Security Manager Architecture and Components › Web Service Request Processing
Web Service Request Processing
SOA Security Manager supports content-level, XML-based security. The following illustration illustrates the flow of data in a simple, single web service implementation secured with SOA Security Manager.
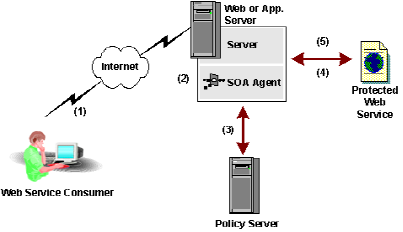
The data in the previous illustration flows as follows:
- A web service consumer (client) application creates a web service request in the form of an XML document and sends it to the web service provider site. An example document could be a purchase order. Credentials and authorization entitlements can be inserted in the message envelope or message body.
- At the web service provider's site, the SOA Agent intercepts the request, based on its action and content type in the HTTP header, as shown in the following XML sample:
POST /CreditRating HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: text/xml
Content-Length: nnnn
SOAPAction:"someURI:CreditRating#GetCreditRating"
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
<!-- request -->
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
- The SOA Agent gathers the sender's credentials from the XML message and passes this information to the CA Policy Server for authentication and authorization.
- The authorized message is passed to the back-end business application for processing.
- Optionally, the back-end application returns a response to the web service requester with the status of the payload (for example, indicating that the purchase order has been accepted and is being processed).
