User directories store user information such as organizational information, user and group attributes, and individual credentials. Multiple user directories in a SOA Security Manager environment often store the same user information, but use different underlying schema and user attribute names to identify them. This results in a disparate view of the same user information from a SOA Security Manager perspective.
The purpose of user attribute mapping is to create a common view of the same user information by defining a universal schema. SOA Security Manager uses this universal schema to resolve user information across multiple user directories.
You can define a user attribute mapping by mapping a common name to the underlying directory schema that identifies a user attribute. Mapping the same common name to the underlying schema of each user directory in the environment results in a universal schema for the user attribute. This creates a common view of the same user information.
Creating such a view lets SOA Security Manager reference user attributes without regard for the directory type, greatly reducing the number of policies or other objects that must be configured to account for multiple user directories. Each user attribute mapping is specific to the user directory in which it is defined.
The following illustrates the basic concept of user attribute mapping:
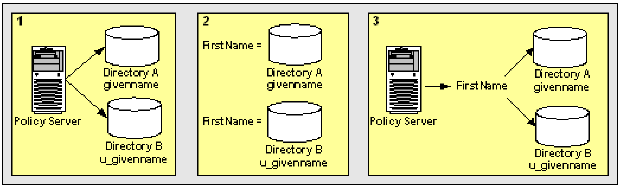
This results in two different representations and views of the same user information.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |