Configuration Guides › Policy Server Configuration Guide › Authentication Schemes › XML Digital Signature Authentication › How XML Digital Signature Authentication Works
How XML Digital Signature Authentication Works
The XML Digital Signature authentication scheme validates XML documents digitally signed with valid X.509 certificates.
The authentication process works as follows:
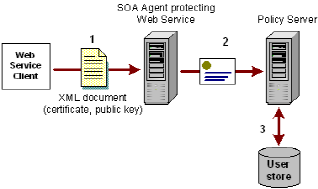
- The web service consumer submits a signed XML document requesting a service. This document includes the required information, including the certificate and the public key.
- The SOA Agent passes the URL of the requested resource to the Policy Server. The Policy Server informs the SOA Agent which credentials need to be collected. The SOA Agent then does the following:
- Verifies the signature and checks that the document is not altered.
The SOA Agent detects two types of signatures:
- Enveloping signature—A signature (defined in a <signature> element) that wraps an entire document. This would be typical of a raw XML document that does not use an enveloping technology, such as SOAP.
- Enveloped signature—A signature embedded in an enveloped document. SOA Security Manager detects only enveloped signatures included in the SOAP headers. If multiple SOAP headers exist, the Agent uses only the first header it detects.
- Checks that the required elements configured as part of the authentication scheme are included with the signature.
- Takes the certificate and passes it to the Policy Server.
- The Policy Server validates the certificate to ensure that it trusts the client by checking that the web service consumer has a valid entry in the user store. This is done using Policy Server’s certificate mapping feature.
To use an X.509 certificate to identify a user, the Policy Server uses a certificate mapping to compare a client’s certificate with the information in the user directory. A certificate mapping defines how data in the certificate is mapped to form a user Distinguished Name (DN), which the Policy Server uses to authenticate the client.
If the web service consumer identified in the certificate is a valid user, the authentication process is complete.
The following illustration shows the process.
More information:
Certificate Mapping for X.509 Client Authentication Schemes
