Configuration Guides › Policy Server Configuration Guide › Authentication Schemes › SAML Session Ticket Authentication › Chain Authentication Service Model Using SAML Session Tickets › How Chain Authentication with SAML Session Tickets Works
How Chain Authentication with SAML Session Tickets Works
In the chain authentication service model, the first web service in the chain is responsible for authenticating all web service consumer requests.
The following illustration shows the communication flow using the SAML Session Ticket authentication in a chain environment.
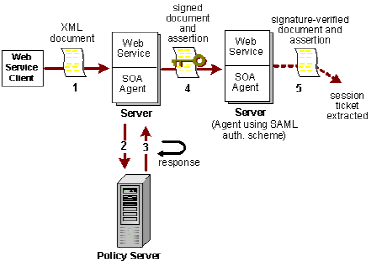
In the previous illustration, the data flows as follows:
- The web service consumer sends a request for access to a protected web Service. This request must be in the form of an XML document.
- The SOA Agent receives the request and the Policy Server authenticates the web service consumer with an authentication scheme other than the SAML Session Ticket scheme, such as XML Document Credential Collector.
The SAML Session Ticket authentication scheme does not protect the first web service in the chain.
- Because the authorizing policy has a SAML Session Ticket response associated with it, after the web service consumer is authenticated and authorized the Policy Server generates a response that it sends to the SOA Agent.
- The SOA Agent uses the response to generate a SAML Session Ticket assertion, which contains an encrypted session ticket and a public key provided by the SOA Agent.
The SOA Agent binds the document by signing it with its private key, places the assertion and the signature into an HTTP header, SOAP envelope header, or cookie, and returns the document and the assertion to the authentication web service.
Note: The assertion is returned to the client, not the response data returned from the Policy Server. That data is returned only to the SOA Agent, which uses it to generate the assertion.
- The web services are configured so that the initial service passes the assertion and the document to the next web service in the chain, which is protected by the SAML Session Ticket authentication scheme.
The assertion is validated by the SOA Agent and the session ticket credentials allow the web service consumer access without reauthenticating.
