WS‑Security responses are typically used to instruct the SOA Agent protecting an authentication web service to create WS‑Security headers and, optionally, to perform XML encryption on those headers and the message content.
The following illustration shows the response process in such an environment.
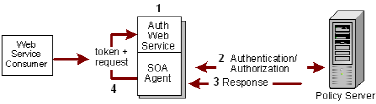
Note: Although any authentication scheme can be configured to obtain credentials from a request, not every authentication scheme is suitable for creating every type of WS-Security token.
However, for a web service that receives requests with XML-encrypted elements, but that does not have the logic to decrypt those requests internally, WS‑Security responses can be used to instruct the SOA Agent to pass the web service decrypted versions of those requests (see TXM_WSSEC_ENCRYPT_PUB_KEY_ROLE).
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |