Configuration Guides › Policy Server Configuration Guide › Authentication Schemes › WS‑Security Authentication › How the Chain Authentication Service Model Works Using WS‑Security
How the Chain Authentication Service Model Works Using WS‑Security
The chain authentication service model is an environment in which the first web service in the chain is responsible for authenticating all web service consumer requests. When the authentication service verifies a requestor’s identity, it add WS‑Security headers to the requesting SOAP document headers and passes the document to downstream web services for further processing.
The following illustration shows the communication flow using WS‑Security tokens in a chain environment.
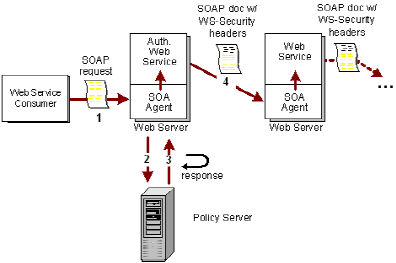
- The web service consumer sends a request for access to a protected web service in the form of a SOAP document.
- The SOA Agent receives the request and the Policy Server authenticates the web service consumer using a supported authentication scheme.
- The XML request goes through the authorization process after authentication. If the web service consumer is authorized, a WS‑Security response attribute associated with the authorizing policy causes the Policy Server to generate a response and send it to the SOA Agent.
The SOA Agent uses the response to generate and add WS‑Security headers to the request’s SOAP headers. The SOA Agent then passes the SOAP request along to the authentication web service.
- The authentication web service sends the SOAP document with WS‑Security headers to the next web service downstream, which is protected using the WS‑Security authentication scheme.
More information:
Supported Authentication Schemes for Producing Each WS-Security Header Type
