Configuration Guides › Policy Server Configuration Guide › Authentication Schemes › SAML Session Ticket Authentication › Multistep Authentication Service Model Using SAML Session Tickets › How SAML Session Ticket Multistep Authentication Using Signed XML Documents Works
How SAML Session Ticket Multistep Authentication Using Signed XML Documents Works
In the multistep authentication service model, one authentication service is responsible for authenticating all web service consumer requests. In this model, the web service consumer must sign each XML document request using a private key associated with the public key that was provided during authentication.
The process that the web service consumer goes through when making a request has two phases:
- Obtaining the assertion
- Using the assertion to access other web services
The following illustration shows the complete flow of data in the multistep authentication service model.
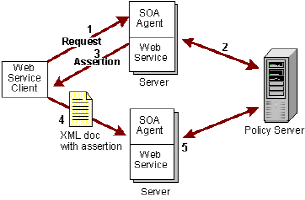
In this illustration, the data flows as follows:
- The web service consumer sends a request. As part of the request, a public key must be made available to the SOA Agent from the request or the policy store.
- The SOA Agent receives the request and passes it to the Policy Server, which authenticates the web service consumer with an authentication scheme other than the SAML Session Ticket scheme, such as XML Document Credential Collector. A session ticket is generated.
The request goes through the authorization process after authentication. If the web service consumer is authorized and a SAML Session Ticket response attribute is associated with the authorizing policy, the Policy Server generates a response and sends it to the SOA Agent.
- The SOA Agent uses the response to generate a SAML Session Ticket assertion, which contains an encrypted session ticket and a public key. The SOA Agent puts the assertion in an HTTP header, SOAP envelope header, or cookie and passes it to the web service, which returns it to the web service consumer.
Note: The assertion is returned to the web service consumer, not the response data returned from the Policy Server. That data is returned only to the SOA Agent, which uses it to generate the assertion.
- For subsequent requests, the web service consumer passes a new signed XML document that includes the assertion to another web Service. The web service consumer signs the document using the private key that corresponds to the public key in the assertion.
These subsequent requests must be in the form of SOAP documents, as required by the SAML Session Ticket authentication scheme.
- The request is granted access to the web service without having to reauthenticate because of the information in the assertion, in effect, providing single sign-on.
