The Policy Server can authorize a user based on the following types of information:
Additionally, the Policy Server can authorize a user based on user attributes provided by a SAML 2.0 Attribute Authority. When a user requests access to a protected resource, the authorizing entity can request additional user attributes to determine whether to grant access to the resource.
In a SAML 2.0 federated network, there are two roles required to authorize a user based on user attributes:
The SAML Attribute Authority adheres to the SAML 2.0 Assertion Query/Request profile. The SAML Attribute Authority relies on the Attribute Service to process a query message and create attribute assertions. These assertions contain user attributes that a SAML Requester uses to authorize access to protected resources. The Attribute Service is part of the Federation Web Services application.
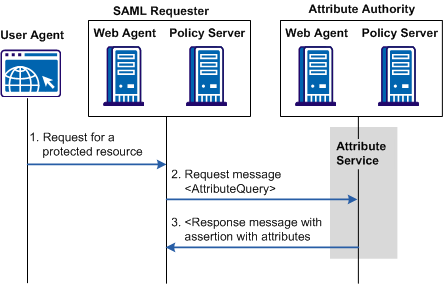
When an entity makes a request to an Attribute Authority, the message contains the user attributes that the requester wants to retrieve. The message also contains the Name ID and the Issuer of the request. The Attribute Service uses the NameID to disambiguate the user so it knows what values to return for the requested attributes. The Attribute Service returns a response message that includes an attribute assertion wrapped in a SOAP message. This response includes the user attributes.
Note: The user does not need to be authenticated at the Attribute Authority. Also, there is no need for a single sign-on relationship between the Authority and the Requester.
The SAML Requester is a SAML entity that uses the SAML 2.0 Assertion Query/Request profile to request attributes for a user. In SiteMinder, the SAML Requester is not a specific service, but a group of Policy Server features that can produce and process <AttributeQuery> messages. The Requester asks for the user attributes from the Attribute Authority because the protected target resource always resides at the SAML requester. The Requester resolves these attributes into variables used by a policy expression.
Note: In a SiteMinder federated environment, the SAML Attribute Authority is the Identity Provider and the SAML Requester is the Service Provider. However, this condition does not have to be the case.
To evaluate an authorization request based on SAML 2.0 user attributes, add a SOA Security Manager attribute type named federation attribute variable to a policy expression. The policy protecting the target resource uses this variable. Based on the policy variable, the SAML Requester sends a query message to the Attribute Authority. This query message contains the Name ID for the SAML entity for which the attributes are being requested. The SAML Attribute Authority returns a response message containing assertions with the attribute statements.
A user must have a session at the SAML Requester; however, the user does not have to log in or authenticate at the Attribute Authority.
The following figure shows how an attribute query is processed.
Note: The SPS federation gateway can replace the Web Agent and Web Agent Option Pack to provide the SiteMinder Federation Web Services application functions. For information about installing and configuring the SPS federation gateway, see the CA SiteMinder Secure Proxy Server Administration Guide.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |