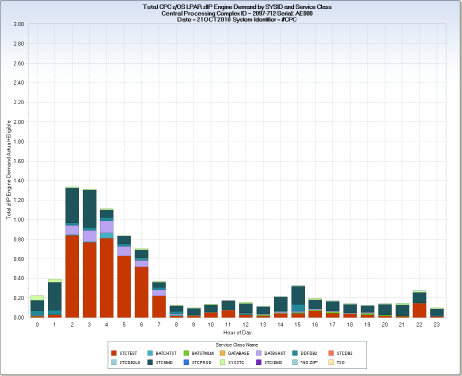

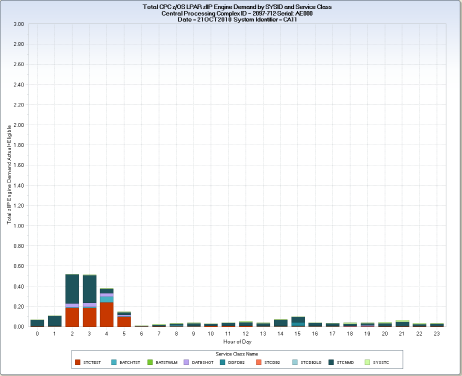
The RMFZIS query charts the hourly total zIIP engine demand (actual zIIP engine use plus zIIP engine eligible use), by WLM Service Class, for the Central Processing Complex (CPC) and individual z/OS LPARs using the shared engine pools of a CPC. Only PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs contribute to these charts because the data containing zIIP engine demand, extracted from the WLMSEC Service Class Resource Consumption file, is derived from RMF type 72-3 records, which only record zIIP engine demand for PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs.
The example shows the following charts:
Both the CPC level and SYSID level charts show total hourly zIIP engine demand, using vertical bars, stacked by WLM Service Class.
Note: A fake Service class named ‘*NO ZAP*’ is created, showing no usage, for hours where there was no zIIP engine demand. This class prevents charts from being produced where hours are missing from the X-axis.
This query is used to examine the WLM Service Classes that execute zIIP engine eligible work. If zIIP usage appears for an LPAR that does not have zIIP engines assigned, then the work is actually executing on expensive CP engines. You may want to reconfigure the LPAR with one or more zIIP engines, or reroute the Service Class workload to execute on an LPAR with zIIP engines. The charts as delivered show total demand—which is the sum of zIIP engine actual use plus any zIIP engine eligible use that executed on CP engines. The two components—actual use and eligible use are available for charting, and can be selected as the Y-axis chart variables if desired. Additionally, you can review the RMFZIC - Daily zIIP Engine Use and Demand by CPC and SYSID query charts. These charts show the breakdown of actual and eligible zIIP engine demand in a single chart.
Note: If a CPC has one or more zIIP engines and no zAAP engines, and has specified ZAAPZIIP=YES in SYS1.PARMLIB, zIIP engines process all specialty engine work—including work that would normally run on zAAP engines. In this environment, all SMF and RMF metrics treat zAAP and zIIP eligible workloads as zIIP eligible. No zAAP actual or eligible demand appears.
Daily Total zIIP Demand by Service Class
ZIPENGT – Total zIIP Engine Demand Actual+Eligible
The vertical bars show total zIIP usage (zIIP actual+eligible CPU time) at the CPC level and for each PR/SM managed z/OS LPAR. For each CPC, the CPC level chart is produced first, with a SYSID value of ‘#CPC’, and is followed by the PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs for that CPC. The CPU times are divided by 3600 to convert from seconds to hours to create the chart variable ZIPENGT. Because one engine can be dispatched a maximum of one hour, per hour, this conversion allows the zIIP engine demand to be represented as physical engine hour equivalents. For example, two zIIP engines could, at full utilization, provide two hours of CPU time in one hour.
HOUR – Hour of Day
TRIM(LPCMOD)||'-'||TRIM(CPCMODID)||'-Serial: '||SUBSTR(CPCSEQNB,12,5);
SUM(ZIPENGA,ZIPENGE) ;
ROUND((SECSUPTM/3600),.001);
ROUND((SECSUPCT/3600),.001) ;
The following modifications can be made to the RMFZIS query:
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |