
The RMFZIC query charts the hourly actual zIIP engine use and zIIP engine eligible use for both the Central Processing Complex (CPC) and the z/OS LPARs using the shared engine pools of a CPC. Only PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs are charted. Non-z/OS LPARs and z/OS LPARs managed by VM are excluded from analysis because the data containing zIIP engine demand is not available.
The example shows the following charts:
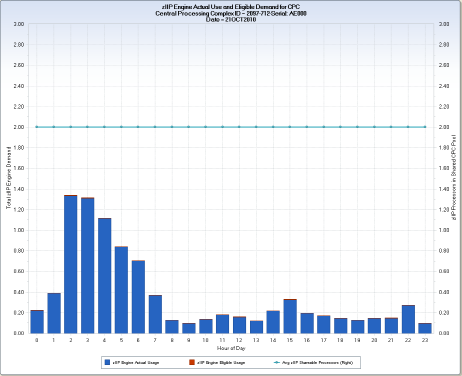
The CPC level chart shows total zIIP engine demand, with the actual use and eligible demand stacked. The horizontal reference line in the CPC level chart shows the number of physical zIIP engines in the CPC shared engine pool.
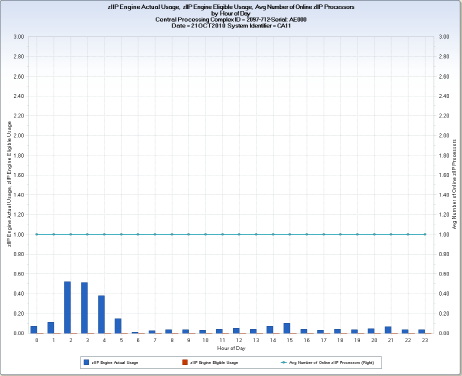
The LPAR level chart shows zIIP engine use and zIIP engine demand as separate vertical bars for each hour of the day. The horizontal reference line in the LPAR level chart shows the number of logical zIIP engines assigned to the LPAR. One LPAR level chart is produced for each LPAR that executed zIIP eligible work.
This query is used to determine if the zIIP engines in a CPC are sufficient to handle the zIIP eligible workload running on z/OS LPARs. Even if no zIIP engines are present in a CPC, the charts show z/OS LPAR zIIP eligible work that executed on CP engines. zIIP engines are less expensive that CP engines. Reducing CP engines in a CPC can reduce software licensing fees. In general, if significant zIIP eligible work is executing on CP engines, it is cost effective to add zIIP engines to the CPC.
Note: If a CPC has one or more zIIP engines and no zAAP engines, and has specified ZAAPZIIP=YES in SYS1.PARMLIB, zIIP engines process all specialty engine work—including work that would normally run on zAAP engines. In this environment, all SMF and RMF metrics treat zAAP and zIIP eligible workloads as zIIP eligible. No zAAP actual or eligible demand appears.
Daily CPC zIIP Eng Use and Demand
ZIPENGA – zIIP Engine Actual Usage
ZIPENGE – zIIP Engine Eligible Usage
This extract shows the total z/OS LPAR zIIP usage at the CPC level. The vertical bars show total zIIP actual and zIIP eligible CPU time for all PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs at the CPC level. The CPU times are divided by 3600 to convert from seconds to hours. Because one engine can be dispatched a maximum of one hour, per hour, this conversion allows the CPU demand to be represented as physical engine dispatch hour equivalents. For example, two zIIP engines could, at full utilization, provide two hours of CPU time in one hour.
PRSMASSP - Avg zIIP Shareable Processors
Average number of physical zIIP engines online in the shared zIIP engine pool.
HOUR – Hour of Day
Daily z/OS System zIIP Eng Use and Demand

ZIPENGA – zIIP Engine Actual Usage
ZIPENGE – zIIP Engine Eligible Usage
This extract shows the z/OS LPAR zIIP usage for the CPCs charted in the CPC level data extract. The vertical bars show total zIIP actual and zIIP eligible CPU time for all PR/SM managed z/OS LPARs at the LPAR level. The CPU times are divided by 3600 to convert from seconds to hours. Because one engine can be dispatched a maximum of one hour, per hour, this conversion allows the CPU demand to be represented as physical engine dispatch hour equivalents. For example, two zIIP engines could, at full utilization, provide two hours of CPU time in one hour.
CPUAVOZP - Avg Number of Online zIIP Processors
Average number of logical zIIP processors online to the LPAR each hour.
HOUR – Hour of Day
TRIM(LPCMOD)||'-'||TRIM(CPCMODID)||'-Serial: '||SUBSTR(CPCSEQNB,12,5);
ROUND((SECSUPTM/3600),.001);
ROUND((SECSUPCT/3600),.001) ;
The following modifications can be made to the RMFZIC query:
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |