To configure roles-based access control to protected resources, a SiteMinder administrator associates an Identity Manager Environment with a Policy Domain in the Policy Server User Interface. The administrator creates a policy to protect an application and associates a role or roles with that policy. Users who have an associated role can access the protected application.
A SiteMinder administrator binds roles to security policies that define how users interact with resources. Policies may link the following objects:
Identify a set of users affected by a policy.
Identify users who have been assigned a set of privileges in Identity Manager.
Identify a resource and the actions that are allowed or denied for the resource. The resource is typically a URL, application, or script.
Determine a reaction to a rule. When a rule fires, responses are returned to a SiteMinder Agent.
Identity Manager uses SiteMinder responses to deliver specific task and role information to a protected resource.
You can bind SiteMinder policies to users, or to roles, or to users and roles. When a user or role member attempts to access a protected resource, SiteMinder uses information in the policy to determine whether to grant access, and to trigger responses.
The following figure illustrates the relationship of policy objects in a role-based policy.
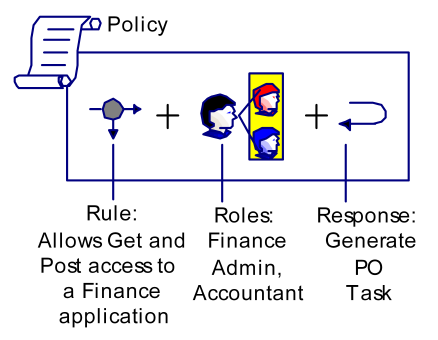
SiteMinder policies are created in policy domains, which logically tie user directories to protected resources. The following figure illustrates the relationship of policy objects in a role-based policy.
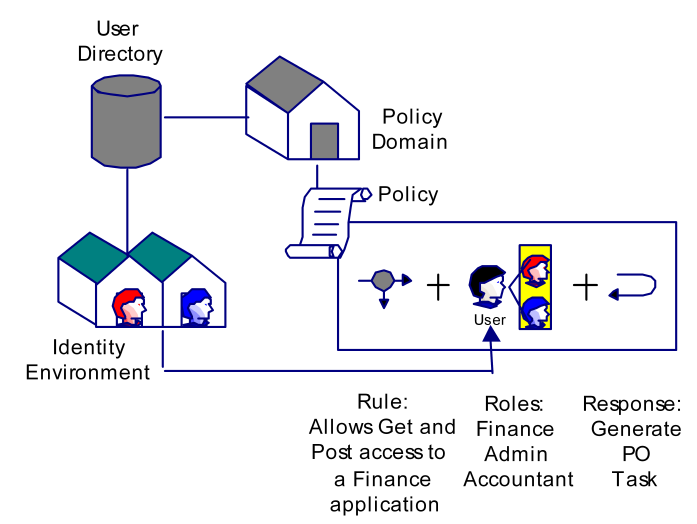
To supply user entitlements to a protected application, a SiteMinder administrator pairs a rule in the application’s policy with a response. The response contains a SiteMinder-generated response attribute that retrieves entitlement information from Identity Manager.
When SiteMinder authorizes a role member for a protected resource, the following events take place:
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |