Configuration Guide › LDAP User Store Management › Directory Structure
Directory Structure
CA Identity Manager supports the following directory structures:
- Hierarchical—Contains a parent organization (root) and suborganizations. The suborganizations may also have suborganizations, which creates a multi-level structure, as shown in the following illustration:
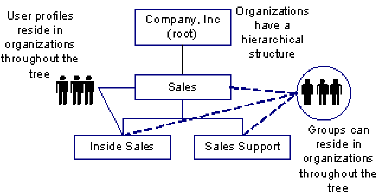
- Flat—User and groups are stored at the search root or in a container one level below the search root. Organizations have a hierarchical structure, as shown in the following illustration of a flat directory structure:
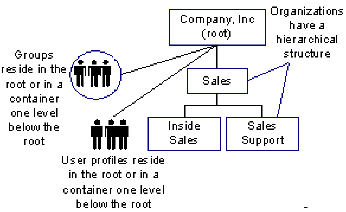
To facilitate user management and delegation in flat directory structures, users and groups belong to logical organizations. The logical organization is stored as an attribute in user and group profiles.
- Flat User—Organizations and groups are stored hierarchically, but users are stored at the search root or in a container one level below the search root, as shown in the following illustration of a flat user directory structure:
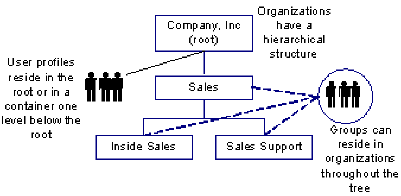
In flat user directory structures, users belong to logical organizations. A user's logical organization is stored as an attribute in a user's profile.
- No organizations—The directory does not include organizations. Users and groups are stored at the search root or in a container one level below the search root. A no-organizations directory structure is shown in the following illustration:
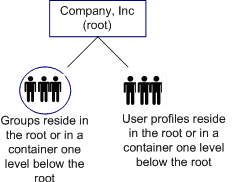
Note: A directory may contain more than one type of structure. For example, user profiles may be stored in a flat structure in one part of the directory and hierarchically in another. To support a hybrid directory structure, create multiple Identity Manager environments.



