When CA Identity Manager and CA RCM integrate, the following communication takes place.
The data is sent to CA Identity Manager using the Java Identity and Access Management (JIAM) API.
This may result in CA RCM completing the following actions in CA Identity Manager:
For example, CA RCM analyzes the Identity Manager role model and notices that there is a new group of users that all have the same privileges in an endpoint. CA RCM creates a new account template for that endpoint in CA Identity Manager, associates that account template with a provisioning role and assigns the provisioning role to users.
CA Identity Manager records these changes in the task persistence database, where they can be viewed in the View Submitted Tasks task.
The following illustration demonstrates the flow of communication.
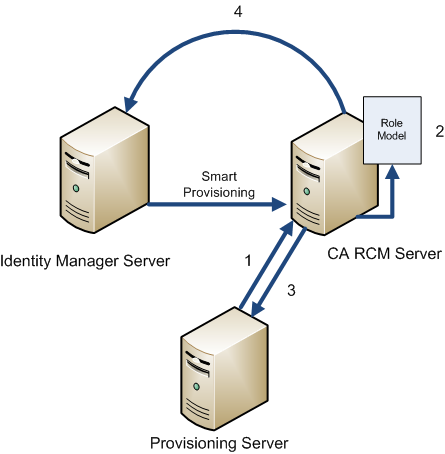
A different process occurs (in addition to the process mentioned above) when support for Smart Provisioning is enabled.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |