You define attribute mapping rules in the Application Attributes Definitions table of the Application Integration dialog. This table is shown in the following figure:
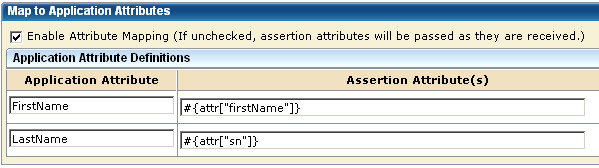
The Application Attribute and Assertion Attribute columns are pre-populated based on assertion attributes specified for the remote Producer or IdP entity, which you configure at this local relying party. The assertion attribute name is entered for the Application Attribute column and the equivalent Unified Expression Language (UEL) string is entered in the Assertion Attribute(s) column.
Administrators or application integrators at the relying party must know the following information to configure attribute mapping:
Gather the names of the application and assertion attributes from the necessary parties before setting up attribute mapping.
The application attributes must reflect the attributes used by the target application so you must modify the default values to suit the application. You obtain the application attributes from an out-of-band communication with the application administrator.
Use the Expression Builder to Build Mapping Rules
The UI provides an expression builder to aid in the construction of mapping rules. Access the expression builder by selecting the slider button (<<) to the right of the Assertion Attribute(s) field. The slider button reveals a blank field and pull-down arrow. Select the arrow to see a list of assertion attributes and special characters that you can use to compose a mapping. Click the slider button (>>) to hide the expression builder.
The following figure shows the Expression Builder menu.
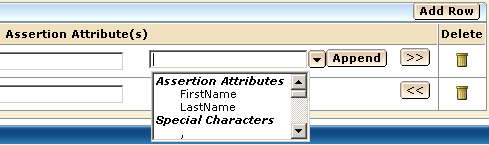
The Assertion Attributes list from the expression builder is pre-populated based on assertion attributes specified for the remote Producer or IdP entity, which you configure at this local relying party. You can specify entries manually as long as you know the attribute is in the assertion. You do not have to use only the options from the expression builder menu.
The Special Characters list contains characters, such as commas and percent signs that you can use to build a mapping rule. You can select a character from the list or enter the character manually.
Important! When you enter assertion attributes in this table, they are case sensitive relative to how the assertion attribute is specified at the remote asserting party. The cases must match. If Federation Manager is at both sides of the partnership, the attributes are specified in the NameID and Attributes step of the remote IdP Partnership wizard. Obtain the assertion attributes in an out-of-band communication with the partner or by importing metadata.
After the mapping rules are defined, Federation Manager places the data in a legacy cookie, an open format cookie, or an HTTP header and sends the data to the application. You specify the delivery method in the Target Application section of the Application Integration dialog.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |