Log collection planning for your network is based upon the number of events per second (eps) you need to process for storage and the length of time you need to retain the data online. (In this sense, online means in an immediately searchable state.) Typically, you have only 30-90 days' worth of data online.
Each network has its own event volumes as a function of the number of devices, device types, and the degree to which network devices and applications like firewalls are tuned to fit the enterprise's event information needs. For example, some firewalls can generate huge volumes of unneeded events based on how they are configured.
We recommend planning your event collection so that your total event volume is spread evenly across your CA Enterprise Log Manager servers without forcing any of them to go beyond the normal constant duty rating. To maintain peak performance at enterprise event volumes, we recommend that you install at least two, federated CA Enterprise Log Manager servers:
The following illustration shows a simple example of this kind of federated CA Enterprise Log Manager network. Two CA Enterprise Log Manager servers, one for reporting and one for collection, handle event traffic from a variety of event sources. Both servers can share data between them for queries, reporting, and alerting.
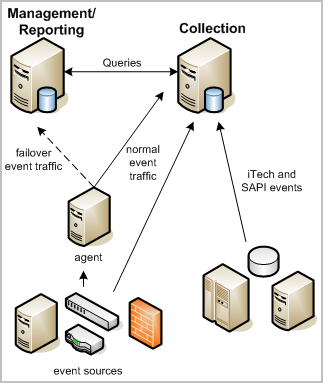
The collection server primarily handles the incoming event log traffic and focuses on database inserts. It uses a short data retention policy of 24 hours or less. An automated script moves stored event logs to a reporting server daily or more often depending on event volume. Federation and the use of federated queries between the two servers ensures that you receive accurate reports from the event logs on both servers.
The reporting server performs several functions:
An automated backup script moves data from the reporting server to a remote server (cold storage). If you decide to restore data from cold storage, you generally will do so on the reporting server. If space on the reporting server is limited, you can also restore to the collection server. Since the collection server does not store large amounts of data and is federated, the report results are the same.
In addition, the reporting server can function as a failover receiver for events collected by a connector on a remote agent, if the collection server stops receiving events for some reason. You can configure failover at the agent level. Failover processing sends events to one or more alternate CA Enterprise Log Manager servers. Failover event collection is not available for events from legacy event sources collected through the SAPI and iTech listeners.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |