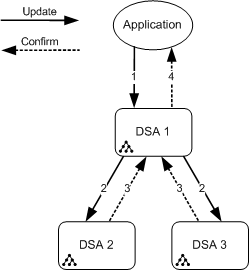
Multiwrite replication uses the Directory System Protocol (DSP), or LDAP via Dxlink to an LDAP server, to send updates in real time to all replication peers in the same region. When a client makes an update request, that update is applied immediately to the local DSA, and then to all other DSAs. The client receives a confirmation response only after all DSAs have responded.
Example: A Simple Multiwrite System
The following diagram shows these steps:
DSA 1 receives the request and immediately applies the update to itself.
Any client can now query any DSA and it gets the same response, because the update has been made to all DSAs.
| Copyright © 2009 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |