The information in a directory can be divided according to a hierarchy. This means that different sections of the directory can be kept in separate locations, to improve resilience and support replication.
Also, directories can be replicated to multiple locations. This allows for quicker searching by many users in different locations, and it also enhances the robustness of the system. If one computer has a hardware problem, the directory on that computer synchronizes itself with its peers on other computers after the hardware problem is fixed.
Example: Company X Acquires Company Y
The Company X call center recently acquired Company Y, which had data about its customers recorded in a directory. The following diagram shows that the Company X directory has been configured to search this new data, without changing the Company Y directory:
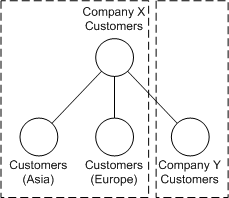
Now, when Peter receives a call from a customer of Company Y, he can use the main Company X directory to look up data about the customer.
| Copyright © 2009 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |