This initial setup of the RLS data can be quite expensive, so the CA DLP infrastructure maintains a connection pool in order to minimise unnecessary load on the database. Once the RLS data is loaded, an entry is put into the connection pool for that user and it is set to 'active' while connected to the database. Once the connection is no longer needed (for example, a search has finished running and returned the data to the iConsole), the entry in the connection pool is set to 'free'. At this point, the RLS data is still in the TMP tables. When the user wants to run another search, the infrastructure checks the connection pool to see if the user has a free connection. The infrastructure then connects to the database and uses the existing RLS data associated to this user meaning that subsequent queries are less expensive. If the user has an active connection and a second connection is required then this will requires a second connection in the connection pool which the will incur the expense of entering another set of rows entered into the TMP tables.
By default, entries in the connection pool are maintained for one hour. Therefore, if the connection is left free for one hour the connection is dropped from the pool and the RLS rows no longer exist in the database so any subsequent searches will require the RLS rows to be reinitialised.
The role of the connection pool is shown in the following diagram.
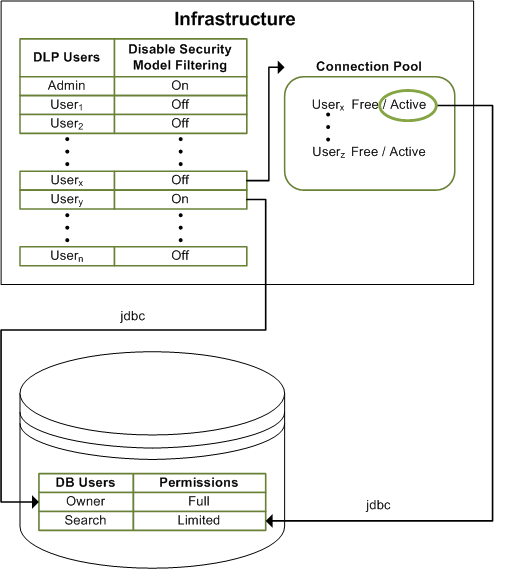
Role of Infrastructure and Connection Pool
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |