The following illustration shows a TCP/IP configuration with two connected z/OS systems and multiple PCs connected to one system using CAICCI TCP/IP client‑server:
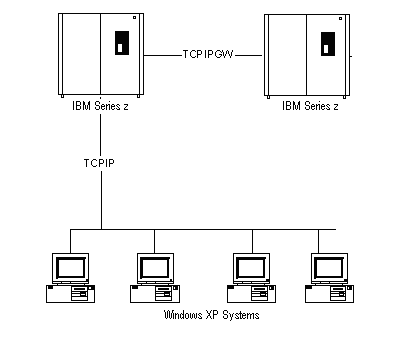
The configuration uses the following CAICCI TCP/IP protocols:
The CAICCI control option member on the respective z/OS system contains the following CAICCI control options:
|
z/OS System |
CAICCI Control Option |
|---|---|
|
A |
SYSID(CCIA) |
|
B |
SYSID(CCIB) |
Defines CAICCI on the z/OS system.
Specifies the CAICCI TCP/IP protocols.
For SSL, the PROTOCOL control options are similar to the following:
PROTOCOL(TCPSSL,1202,1,CCIx,16384) PROTOCOL(TCPSSLGW,1721,1,CCIx,16384)
Specifies the remote node.
To use the logical host names, CCIA.COM and CCIB.COM, the TCP/IP environment must be able to reference a TCP/IP domain name server (DNS) or has a host name table that can translate the specified names to IP addresses.
For best performance, the data packet size (8192 in this example) should be slightly smaller than the maximum transmission unit (MTU) supported by your TCP/IP configuration.
Connects the system to the remote node.
Note: For more information about CAICCI control options, see the Reference Guide.
Note: Similar configuration is suitable for connecting other full‑function CAICCI platforms to the mainframe, including UNIX and Windows.
For the PC-to-mainframe client‑server configuration, no further changes are required on the mainframe. In a client-server configuration, the remote PCs initiate the connections, which require CAICCI be configured on the PCs.
| Copyright © 2012 CA. All rights reserved. | Tell Technical Publications how we can improve this information |