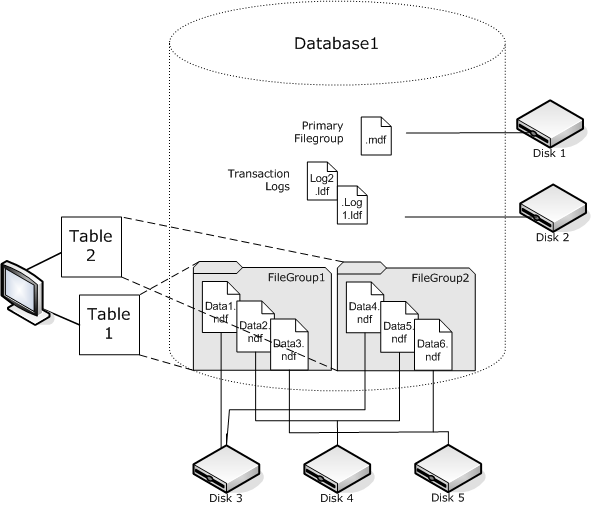
All databases have a primary FileGroup. By default, the Primary Data File and any Secondary Data Files you create are stored in the Primary FileGroup. However, you may create user-defined FileGroups to store your Secondary Data Files. Use FileGroups to manage database performance, growth, and data allocation.
Note: A file can be part of only one FileGroup. A file or FileGroup can be used by only one database. Transaction log files are not contained in FileGroups at all.
The following diagram illustrates a database with six user-defined Secondary Data Files (.ndf) grouped in two user-defined FileGroups and stored on three separate disks. You can create a table on each FileGroup so that any queries against the data in a table can then be allocated across the three disks in parallel, to improve performance. Note also that the Transaction Log and Primary Data Files are stored separately from user data.

With SQL Server 2005, Microsoft added full-text search enhancements that let you back up and restore one or more full-text catalogs. You can now backup catalogs with, or separate from, your database data.
A database can hold one or many full-text catalogs, but a catalog can only belong to one database. A full-text catalog holds the full-text indexes created for one or more tables, but a table can have only one full-text index.
Full-text catalogs are not stored in regular data files, but are still treated as files in the database are therefore included in the database file set you can back up. You can perform a complete (full) or a differential backup and restore of a full-text catalog. An individual full-text index created for a particular table can be assigned to a FileGroup and then backed up or restored as usual.
In SQL Server 2008, Microsoft introduced Filestream storage. Filestream data are often very large and unstructured objects that typically reside outside of a database, such as text documents, images, videos or music files. In SQL Server 2008, Filestream data is stored in separate FileGroups that contain only file system directories instead of the Filestream objects themselves.
Note: Large FILESTREAM collections may take significant amounts of time to estimate, causing property list generation to be slow.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |