Within the CA 2E product, external functions can be defined with an object attribute of either PGM or a MOD. When compiled, these functions become one of two i OS object types-respectively, a *PGM (executable program) or a *MODULE (non-executable module).
A *PGM object can be directly called, either from a command-line or from another program (assuming the correct parameters are passed). By contrast, a *MODULE object must first be 'bound' into an executable program.
Earlier releases of CA 2E provided the following ILE-specific functionality:
Note: Developers could then define certain external functions (typically ones that would never be called from a command line, such as SELRCD's) as modules. Any programs that called these functions (EDTFIL's, etc.) would include a copy of the module object. In ILE terms, this is known as bind-by-copy.
For example, the following diagram shows the use of three PGM functions calling two MOD functions and the resulting *PGM objects containing copies of the *MODULE objects:
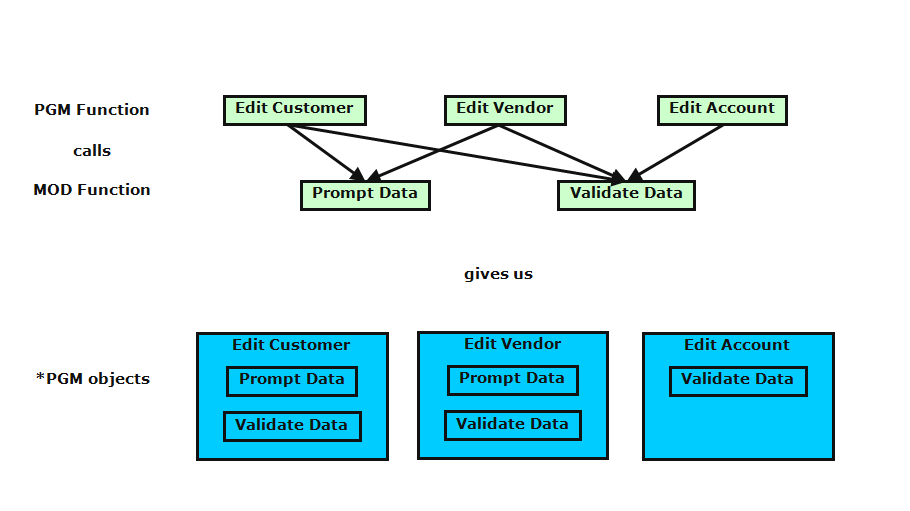
This has a number of benefits:
However, if a module is bound into a program and the code within the module function needs to be changed, the *MODULE must be recompiled and then any programs that bind that module must be changed to include the new copy of the module-typically this would be done by regenerating/recompiled the PGM function in a 2E model, although the i OS UPDPGM command can be run from outside the model environment.
Note: Although there are fewer *PGM objects, they are larger than if they did not contain a copy of the module.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Tell Technical Publications how we can improve this information |